Human Resources Observational Study
Prepared By: [Your Name]
I. Introduction
Human Resources (HR) plays a critical role in managing an organization's workforce, ensuring employee satisfaction, fostering productivity, and promoting a positive work environment. This observational study explores the relationship between HR practices and employee performance, focusing on recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, and employee retention. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how strategic HR functions impact employee behavior, motivation, and overall organizational success.
II. Recruitment and Selection
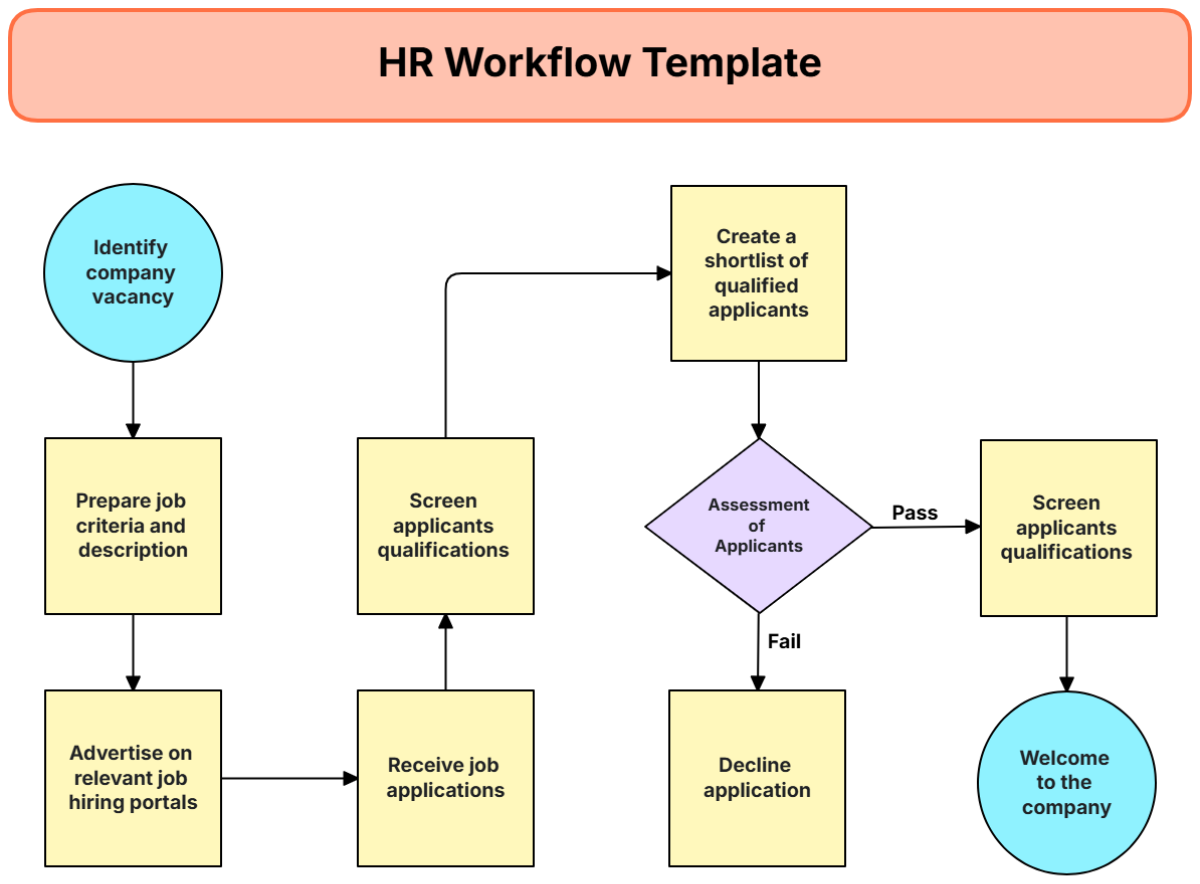
Recruitment and selection are fundamental HR functions aimed at attracting and hiring the right talent. This process involves identifying vacancies, attracting suitable candidates, and selecting the most qualified individuals.
A. The Recruitment Process
Recruitment is the first step in building an organization's human capital. Effective recruitment strategies ensure that businesses have a pool of talented candidates ready to contribute to the company's success.
B. Internal Recruitment
Internal recruitment is the process of filling vacancies within an organization by promoting or transferring existing employees. This approach offers several advantages:
Cost-effectiveness: It eliminates the need for external advertising.
Employee retention: Promoting from within enhances employee loyalty and morale.
Familiarity with the company culture: Internal candidates already understand the organization’s goals and culture, reducing onboarding time.
C. External Recruitment
External recruitment involves seeking candidates from outside the organization. It allows for a broader talent pool but requires more time and resources.
Diversity: External recruitment fosters a more diverse workforce.
New perspectives: New employees bring fresh ideas and innovations.
Skill gaps: External candidates may possess skills not found within the existing workforce.
D. Selection Methods
Selection is the process of identifying the best candidate for a position. Various methods are used in selection, including:
Interviews: These are the most common selection methods, allowing the employer to assess a candidate's communication skills, experience, and cultural fit.
Psychometric testing: These tests measure cognitive abilities and personality traits to ensure the candidate aligns with the job's requirements.
Assessment centers: Group exercises, presentations, and role-play activities help gauge candidates' teamwork and problem-solving abilities.
Table 1: Advantages and Disadvantages of Selection Methods
Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Interviews | Face-to-face interaction, subjective assessment | Can be biased, time-consuming |
Psychometric testing | The Objective measure of abilities reduces biases | Can be costly, candidates may find tests stressful |
Assessment centers | Real-world scenario evaluation, teamwork observation | Expensive, time-intensive |
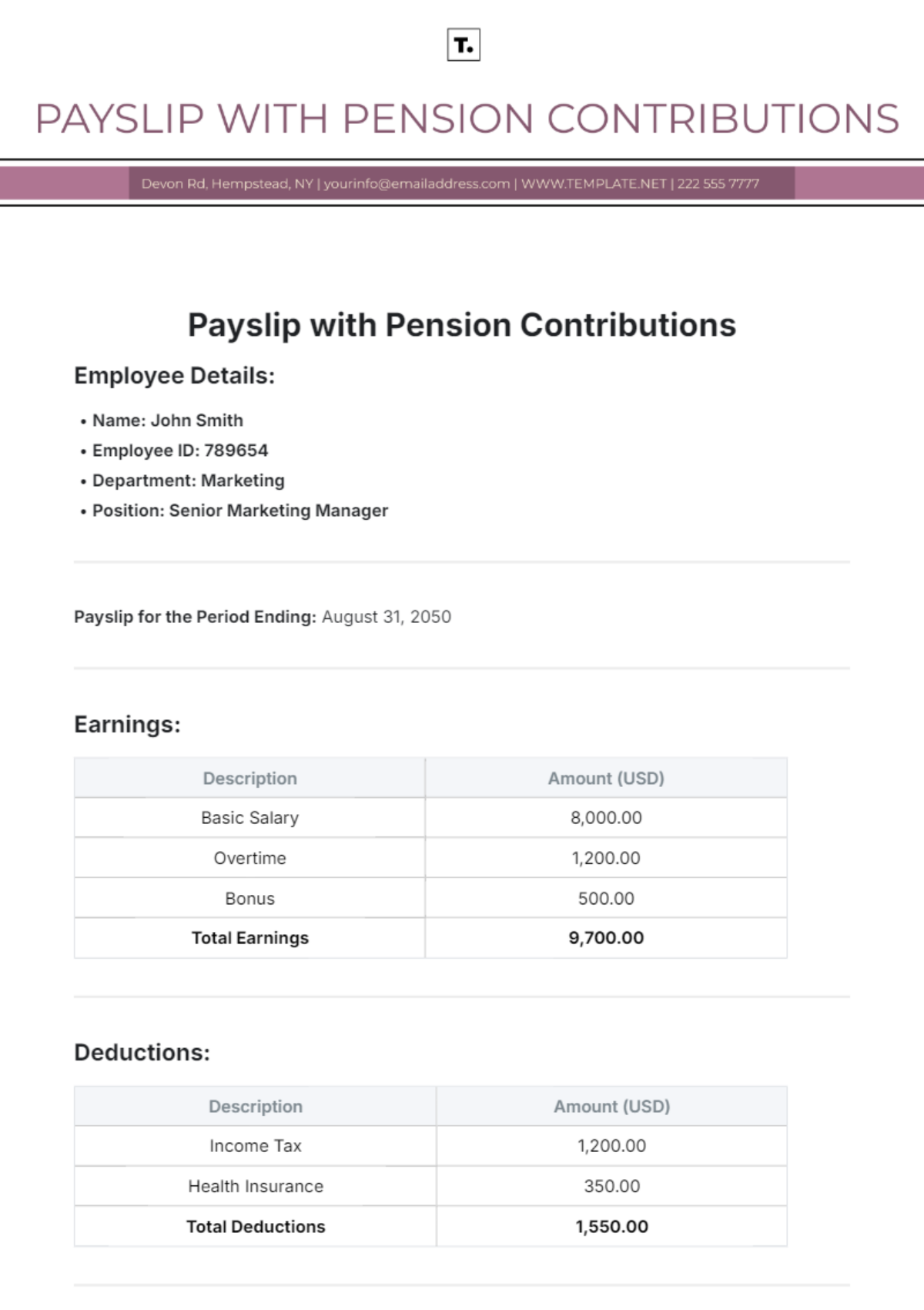
E. Observation: Impact of Recruitment and Selection on Employee Performance
In this study, we observed that organizations with well-structured recruitment and selection processes reported a higher level of job satisfaction and employee engagement. Employees hired through rigorous selection procedures showed greater alignment with organizational goals, which contributed positively to overall performance.
III. Training and Development
Training and development are crucial HR functions that enable employees to acquire new skills, enhance their knowledge, and improve their overall performance. A strong emphasis on continuous learning helps organizations stay competitive and innovative.
A. Types of Training
On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training involves teaching employees how to perform their tasks while they are working. It is a hands-on method that allows employees to learn in real time, promoting practical skills.
Advantages:
Immediate application of skills.
Lower costs compared to formal training programs.
Builds confidence in employees as they work on actual tasks.
Off-the-Job Training
Off-the-job training takes place outside the work environment, often in a classroom or online setting. This method provides employees with new knowledge and skills, usually through workshops, seminars, or e-learning platforms.
Advantages:
Focus on learning without the pressure of performing work tasks.
Access to expert instructors and a structured learning environment.
More comprehensive training materials.
B. Development Programs
Development programs are long-term initiatives that focus on preparing employees for future roles, particularly leadership positions. Examples include:
Leadership development programs: These programs train employees to take on managerial roles through coaching, mentoring, and workshops.
Technical skills development: These focus on enhancing an employee’s proficiency in specialized areas such as IT, engineering, or finance.
C. Observation: Correlation Between Training and Employee Productivity
The organizations that provided robust training programs saw significant improvements in employee productivity. Employees who received continuous training felt more confident in their abilities and were more motivated to contribute to their teams. Additionally, skills development led to higher job satisfaction, which in turn reduced turnover rates.
IV. Performance Management
Performance management is a continuous process where HR ensures employees’ activities and outputs are aligned with the organization’s goals. This process includes setting expectations, monitoring performance, providing feedback, and facilitating improvement.
A. Key Components of Performance Management
Goal Setting
Setting clear and measurable goals is the first step in performance management. Goals should be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and communicated clearly to employees.
Advantages:
Provides employees with direction and purpose.
Facilitates accountability and focus on key results.
Encourages employee growth through achievable targets.
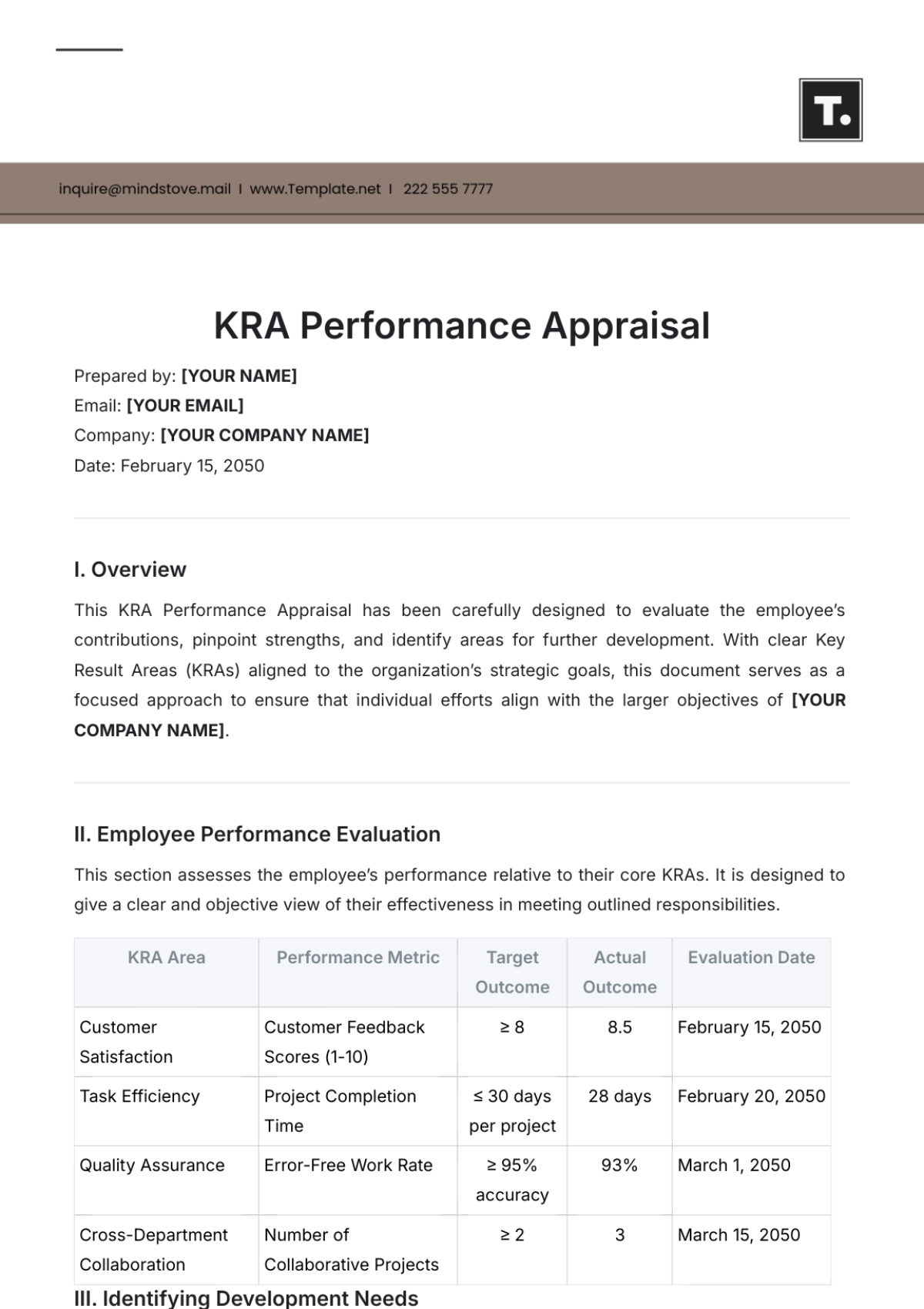
B. Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisals assess an employee’s job performance against the predefined goals. Common methods include:
360-degree feedback: Feedback is gathered from multiple sources, including peers, subordinates, and managers, providing a holistic view of performance.
Self-assessment: Employees evaluate their performance, promoting self-awareness and reflection.
Manager evaluation: A direct supervisor evaluates an employee’s performance based on observed behavior and results.
Table 2: Methods of Performance Appraisal
Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
360-degree feedback | Comprehensive, encourages team collaboration | Can be time-consuming, potential for bias |
Self-assessment | Promotes self-awareness, encourages employee initiative | May not be objective, prone to overestimation |
Manager evaluation | Provides clear feedback from leadership | Can be subjective, dependent on the manager’s skills |
C. Observation: Performance Management and Employee Engagement
In the organizations studied, a well-executed performance management system had a positive effect on employee engagement. Employees who received regular feedback and were involved in the goal-setting process were more motivated and showed a higher level of job satisfaction. In contrast, those without a clear performance management structure often felt disconnected from the organization’s objectives.
V. Employee Retention
Employee retention focuses on keeping talented employees in the organization and reducing turnover rates. High turnover can lead to increased costs, loss of institutional knowledge, and reduced productivity.
A. Retention Strategies
Competitive Compensation and Benefits
Providing competitive salaries and benefits is a key factor in retaining employees. This includes not only base pay but also additional perks such as health insurance, retirement plans, and bonuses.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Employees are more likely to stay with an organization if they see opportunities for career growth. Promotion from within, mentorship programs, and lateral moves can all contribute to a sense of progression and development.
Work-Life Balance
Offering flexible work arrangements, such as remote work, flexible hours, or compressed work weeks, helps employees balance their professional and personal lives. A good work-life balance is associated with higher job satisfaction and lower stress levels.
B. Observation: The Effect of Retention Strategies on Employee Turnover
Our observations revealed that organizations with strong retention strategies had significantly lower turnover rates. Companies that invested in their employees’ growth and provided a supportive work environment retained their best talent, leading to higher productivity and a more stable workforce.
VI. Conclusion
This observational study demonstrates that effective HR practices, particularly in recruitment, training, performance management, and retention, have a direct and measurable impact on employee performance. By fostering a supportive and engaging work environment, organizations can enhance productivity, reduce turnover, and achieve long-term success. HR departments that align their strategies with organizational goals and employee needs are well-positioned to build a highly motivated and high-performing workforce.