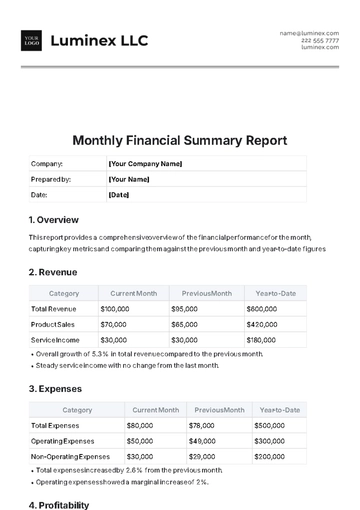
Free Financial Reporting SOP

Introduction
This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is designed to establish a comprehensive framework for the financial reporting process within our company. It aims to ensure consistency, reliability, and transparency in the creation, review, and dissemination of financial reports.
Purpose of the SOP
The primary purpose of this SOP is to:
Provide clear guidelines on the preparation, review, and distribution of financial reports.
Ensure compliance with current financial reporting standards and regulatory requirements.
Facilitate timely and accurate financial decision-making by providing relevant and reliable financial data.
Enhance the efficiency of the financial reporting process through standardized procedures.
Scope of the SOP
This SOP applies to all aspects of financial reporting within the organization, including:
The roles and responsibilities of the finance team and management in the financial reporting process.
Document control and reporting calendar to maintain timely and organized financial reporting.
Procedures for accurate data collection, report preparation, and review.
Approval workflows to ensure the integrity and accuracy of financial reports.
Distribution protocols for both internal and external stakeholders, ensuring the secure and efficient dissemination of financial information.
Continuous Improvement
This SOP is a living document and will be reviewed and updated regularly to adapt to the changing financial standards, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements. Feedback from users of the SOP will be crucial in refining and enhancing the procedures outlined.
By adhering to this SOP, our company commits to upholding the highest standards of financial reporting, ensuring that we remain accountable, transparent, and forward-looking in all our financial endeavors. This commitment is vital for maintaining our reputation, facilitating growth, and ensuring the long-term success of the organization in a highly dynamic and competitive global environment.
Roles and Responsibilities
Finance Team
Data Collection: Gather financial data from all relevant departments, encompassing sales figures, expenses, payroll data, and other pertinent financial transactions.
Data Validation: Ensure the accuracy and integrity of collected data. Implement checks and balances to mitigate errors.
Report Preparation: Compile the data into standard financial reports like income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and budget variance reports, relevant for the fiscal year [2050].
Analysis: Conduct basic analysis of the financial data, highlighting trends, variances, and potential areas of concern.
Finance Team Responsibility
Position | Responsibility | Frequency |
Accountant | Data Collection & Validation | Daily |
Financial Analyst | Data Analysis & Report Drafting | Weekly |
Controller | Final Report Preparation | Monthly |
Management
Primary Duties:
Review and Approval: Thoroughly review reports prepared by the finance team for accuracy and adherence to required standards and compliance.
Strategic Decision Making: Utilize the financial reports for informed strategic decisions.
Compliance and Standards Oversight: Ensure all financial reporting is in line with relevant legal standards and internal policies.
Document Control
Document control is essential for maintaining the integrity and traceability of financial reports. This outlines the procedures for managing financial documents for the year [2050] and onwards.
Procedure:
Document Creation: All financial reports must be generated using standard templates to ensure consistency.
Document Tracking: Log each report in the Document Control Register, recording the report name, creation date, version number, and author.
Document Control Register Example
Report Name | Creation Date | Version | Author |
Monthly Income Statement | 2050-01-01 | V1.0 | [Name] |
Quarterly Budget Analysis | 2050-03-15 | V2.1 | [Name] |
Version Control: Save each revised report as a new version to maintain a clear history of changes.
Access Control: Restrict report access to authorized personnel only, ensuring confidentiality and data integrity.
Archiving: Archive all reports for a minimum of seven years (or as per legal requirements) for historical and legal reference.
Archiving Procedure
Label each report with the date and type of report.
Store in a secure, organized digital archive.
Maintain a physical backup, if necessary.
Reporting Calendar
Effective financial reporting relies on strict adherence to a well-defined reporting calendar. This calendar is crucial for ensuring timely preparation, review, and submission of financial reports, especially in the advanced fiscal landscape of [2050] and beyond.
Annual Reporting Schedule
The annual reporting schedule outlines key dates and deadlines for the fiscal year. It's essential for planning and allocating resources throughout the year.
Report Type | Deadline | Description |
Q1 Report | 2050-04-30 | First-quarter financial summary |
Monthly and Quarterly Reporting
Monthly and quarterly reports provide ongoing insight into the company's financial health and are pivotal for short-term decision-making.
Report Type | Frequency | Deadline |
Income Statement | Monthly | 10th of the following month |
Data Collection
Data collection is a critical phase in financial reporting. It involves gathering, verifying, and organizing financial data from various sources.
Data Collection Sources
Identifying and accessing the right data sources is fundamental to accurate financial reporting.
Source | Data Type | Collection Method |
Sales Department | Sales Figures | Automated Sales Reporting System |
HR Department | Payroll Data | HR Information System |
Operations | Operational Expenses | Expense Tracking Software |
Data Collection Procedures
Proper procedures must be established to ensure the consistency and reliability of data collected.
Data Verification and Validation
Data verification and validation are crucial to prevent errors in financial reporting.
Initial Verification: Perform an initial check of data for obvious errors or inconsistencies.
Cross-Verification: Cross-check data with related records.
Final Validation: The finance team should conduct a final review of the data before it is used in report preparation.
Report Preparation
The preparation of financial reports is a critical process, requiring meticulous attention to detail and adherence to financial reporting standards. This process becomes even more crucial in the context of the advanced fiscal industry in 2050.
Income Statement Preparation
The income statement is a fundamental report that reflects the company's financial performance over a specific period.
Income Statement Preparation Steps
Gather Revenue Data: Compile all revenue streams, including sales, returns, and other income.
Summarize Expenses: Document all operational, administrative, and other relevant expenses.
Calculate Net Income: Subtract total expenses from total revenue to determine net income.
Review and Adjustments: Conduct a thorough review for accuracy and make necessary adjustments.
Balance Sheet Preparation
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company's financial position at a specific point in time.
Balance Sheet Preparation Steps
List Assets: Detail all current and long-term assets, including cash, investments, inventory, and property.
List Liabilities: Document all current and long-term liabilities like loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses.
Calculate Equity: Determine shareholder equity by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
Final Review: Ensure the balance sheet balances and conduct a final review.
Report Review and Analysis
Once the financial reports are prepared, they undergo a rigorous review and analysis process. This ensures not only the accuracy of the reports but also provides valuable insights into the company's financial health.
Internal Review
The internal review is the first line of defense against inaccuracies in financial reporting.
Preliminary Review: Conducted by the author of the report to check for basic errors.
Peer Review: A different member of the finance team reviews the report for a secondary check.
Management Review: Senior management reviews the report for strategic insights and overall accuracy.
Financial Analysis
Financial analysis involves interpreting the data in the reports to make informed business decisions.
Key Financial Analysis Areas
Profitability Analysis: Assessing the company's ability to generate profit.
Liquidity Analysis: Evaluating the company's ability to meet short-term obligations.
Solvency Analysis: Examining the company's capacity to sustain operations long-term.
Operational Efficiency: Analyzing operational processes and their impact on the financials.
Approval Process
The approval process for financial reports is a critical step to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information being disseminated. This process is particularly vital in the context of the advanced fiscal industry of [2050] and beyond, where financial decisions are based on complex data and require stringent oversight.
Approval Workflow
The approval workflow is a structured process that involves several layers of review and sign-off to ensure the integrity of the financial reports.
Initial Approval: The finance team's manager reviews and gives initial approval.
Departmental Review: Relevant department heads review the report for accuracy from their department's perspective.
Executive Review: The CFO or equivalent senior executive reviews the report for overall accuracy and strategic alignment.
Final Sign-off: The CEO or a designated board member provides the final sign-off, officially approving the report for distribution.
Documentation of Approval
Each stage of the approval process must be documented for accountability and audit purposes.
Report Distribution
The distribution of financial reports is a sensitive process, as these documents contain confidential and critical business information. Proper channels and protocols must be in place to ensure secure and efficient distribution.
Internal Distribution Methods
Email: Secure, encrypted email for quick distribution to authorized personnel.
Intranet: Posting on the company's secure intranet for easy access by relevant parties.
Meetings: Presentation in management and departmental meetings for collaborative review and discussion.
External Distribution
External distribution involves sharing financial reports with stakeholders outside the organization.
Regulatory Bodies: Submit required reports to regulatory bodies as per statutory deadlines.
Investors and Shareholders: Distribute reports to investors and shareholders through secure portals or as part of investor relations communications.
Public Disclosure: Release public versions of certain financial reports, like annual reports, on the company's website and through press releases, ensuring compliance with disclosure regulations.
Distribution Security Measures
Use of encryption and secure channels for electronic distribution.
Verification of recipient identities to prevent unauthorized access.
Maintenance of distribution logs for audit and tracking purposes.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Streamline your financial reporting processes with Template.net's Financial Reporting SOP Template. This editable and customizable document provides a standard operating procedure for financial reporting. Ideal for finance teams, it ensures accuracy, consistency, and compliance with regulatory standards, enhancing the reliability and efficiency of financial reporting in your organization. Download now!
You may also like
- Sales Report
- Daily Report
- Project Report
- Business Report
- Weekly Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Report Layout
- Report Design
- Progress Report
- Marketing Report
- Company Report
- Monthly Report
- Audit Report
- Status Report
- School Report
- Reports Hr
- Management Report
- Project Status Report
- Handover Report
- Health And Safety Report
- Restaurant Report
- Construction Report
- Research Report
- Evaluation Report
- Investigation Report
- Employee Report
- Advertising Report
- Weekly Status Report
- Project Management Report
- Finance Report
- Service Report
- Technical Report
- Meeting Report
- Quarterly Report
- Inspection Report
- Medical Report
- Test Report
- Summary Report
- Inventory Report
- Valuation Report
- Operations Report
- Payroll Report
- Training Report
- Job Report
- Case Report
- Performance Report
- Board Report
- Internal Audit Report
- Student Report
- Monthly Management Report
- Small Business Report
- Accident Report
- Call Center Report
- Activity Report
- IT and Software Report
- Internship Report
- Visit Report
- Product Report
- Book Report
- Property Report
- Recruitment Report
- University Report
- Event Report
- SEO Report
- Conference Report
- Narrative Report
- Nursing Home Report
- Preschool Report
- Call Report
- Customer Report
- Employee Incident Report
- Accomplishment Report
- Social Media Report
- Work From Home Report
- Security Report
- Damage Report
- Quality Report
- Internal Report
- Nurse Report
- Real Estate Report
- Hotel Report
- Equipment Report
- Credit Report
- Field Report
- Non Profit Report
- Maintenance Report
- News Report
- Survey Report
- Executive Report
- Law Firm Report
- Advertising Agency Report
- Interior Design Report
- Travel Agency Report
- Stock Report
- Salon Report
- Bug Report
- Workplace Report
- Action Report
- Investor Report
- Cleaning Services Report
- Consulting Report
- Freelancer Report
- Site Visit Report
- Trip Report
- Classroom Observation Report
- Vehicle Report
- Final Report
- Software Report