Free Household Budget Rules

Prepared by: [Your Name]
Date: [Date]
I. Introduction
Effective financial management is essential for achieving both short-term and long-term financial stability. By carefully tracking income and expenses, setting clear savings goals, and prioritizing financial commitments, individuals can make informed decisions that lead to financial success. This comprehensive guide outlines a structured approach to managing finances, covering everything from identifying income sources to regular budget reviews. Whether you're looking to save for a significant purchase, pay off debt, or invest for the future, these steps will help you build a solid financial foundation.
II. Income Allocation
II.I Identify All Sources of Income
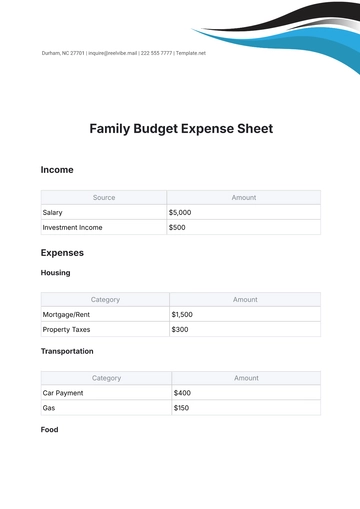
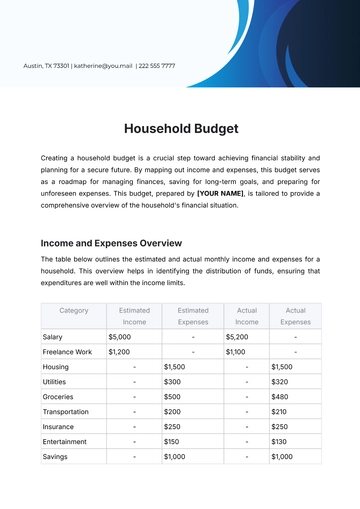
To create an accurate budget, it’s vital to account for all sources of income, including primary salaries, secondary incomes, bonuses, freelance earnings, and rental income.
II.II Categorize Income
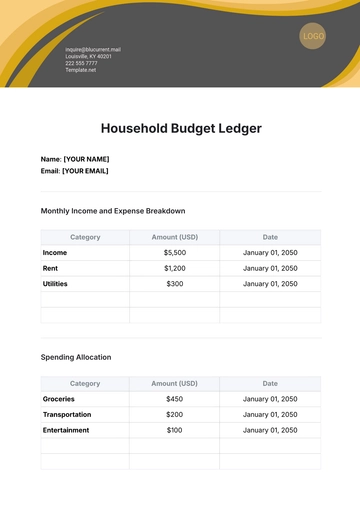
Classify income into fixed, variable, and irregular categories. This helps in understanding the consistency of earnings and planning for future financial needs.
III. Expense Tracking
III.I Identify Fixed Expenses
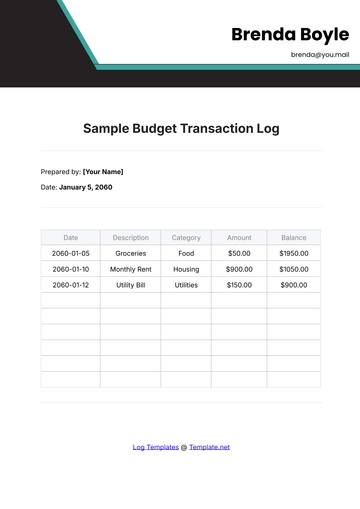
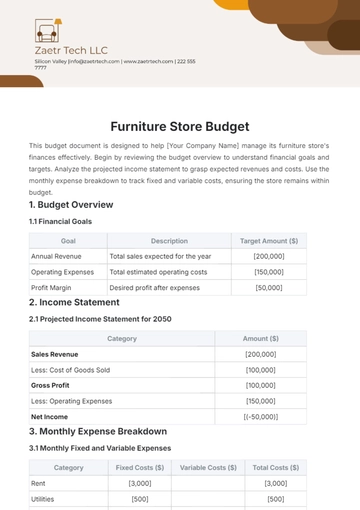
Track all recurring monthly expenses such as mortgage, utilities, insurance, loan payments, and subscriptions. These are essential for maintaining daily life.
III.II Identify Variable Expenses
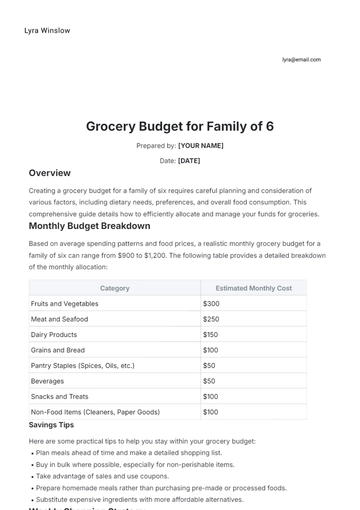
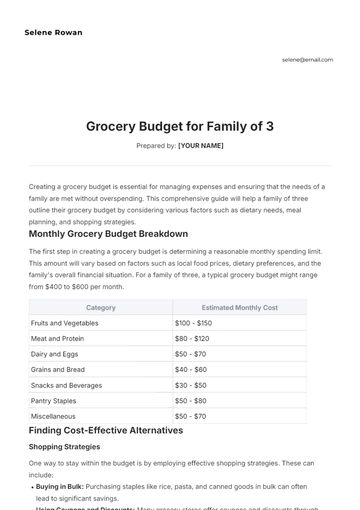
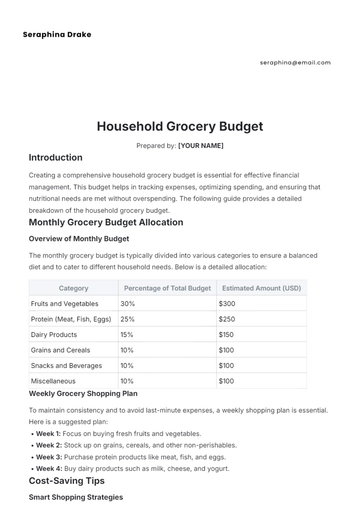
Monitor expenses that vary monthly, including groceries, dining out, entertainment, transportation, and healthcare costs.
III.III Track Irregular Expenses
Plan for less frequent expenses like car maintenance, house repairs, vacations, gifts, and annual fees. These can impact the budget significantly if not anticipated.
IV. Setting Savings Goals
IV.I Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is crucial for handling unexpected financial setbacks. Aim to save enough to cover 3-6 months of living expenses.
IV.II Short-Term Goals
Set savings goals for short-term needs and desires, such as new appliances, home improvements, upcoming vacations, and electronics.
IV.III Long-Term Goals
Establish long-term financial goals, including retirement savings, college funds, home ownership, and investment portfolios.
V. Prioritizing Financial Commitments
V.I Essential vs. Non-Essential Expenses
Differentiate between essential expenses (housing, utilities, food, transportation) and non-essential expenses (dining out, entertainment, luxury items) to prioritize spending.
V.II Debt Repayment
Focus on paying off high-interest debts first, such as credit card debt and high-interest loans, to reduce financial burden.
V.III Regular Savings Contributions
Ensure consistent savings contributions through automatic transfers, investments in mutual funds and stocks, and funding retirement accounts.
VI. Budget Review and Adjustment
VI.I Monthly Budget Review
Regularly review the budget to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
VI.II Annual Financial Review
Conduct a comprehensive annual review to evaluate financial health and realign goals.
VI.III Family Meetings
Hold family meetings to discuss financial challenges, review spending patterns, and update goals and priorities.
VII. Conclusion
In summary, effective financial management requires diligent tracking of income and expenses, setting realistic savings goals, and making informed financial decisions. By following a structured approach, individuals can achieve financial stability and work towards their long-term aspirations. Regular reviews and adjustments ensure that the financial plan remains aligned with changing circumstances and priorities. With a strong financial foundation, individuals can confidently navigate the complexities of personal finance and secure their future.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Manage your finances effortlessly with the Household Budget Rules Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable template provides clear guidelines for family budgeting. Editable in our Ai Editor Tool, it can be tailored to your specific financial goals. Ideal for promoting financial responsibility, this template is essential for maintaining transparency and control over your household budget.
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising