How to Create a School Budget
Prepared by: [Your Name]

Creating a school budget is a critical task for school administrators, as it ensures the efficient allocation of resources and alignment with educational goals. A well-prepared budget can support academic achievement, foster a positive learning environment, and address the diverse needs of students. This article outlines a comprehensive guide on how to create a school budget, touching on planning, implementation, and monitoring processes.
Understanding the Importance of a School Budget
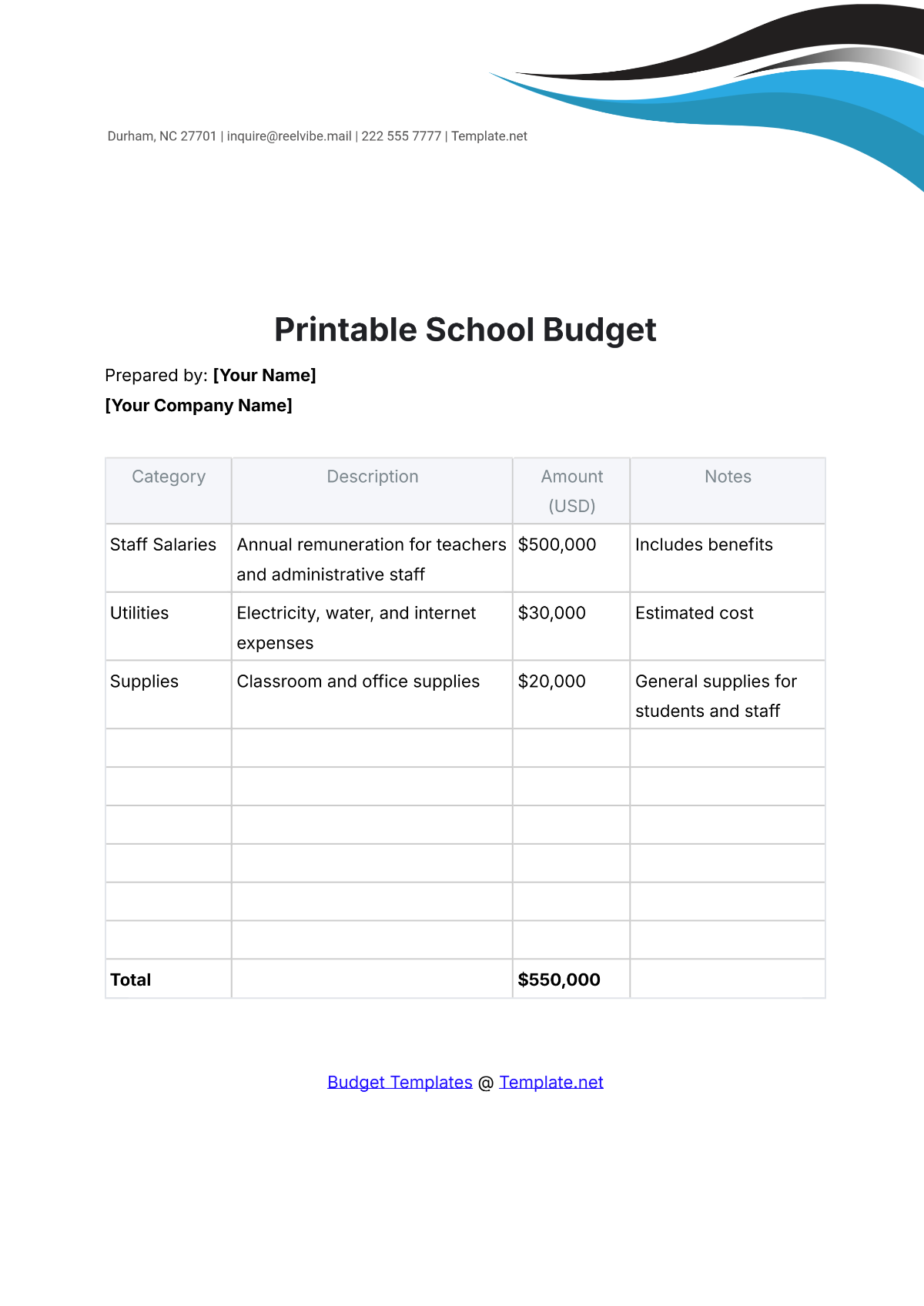
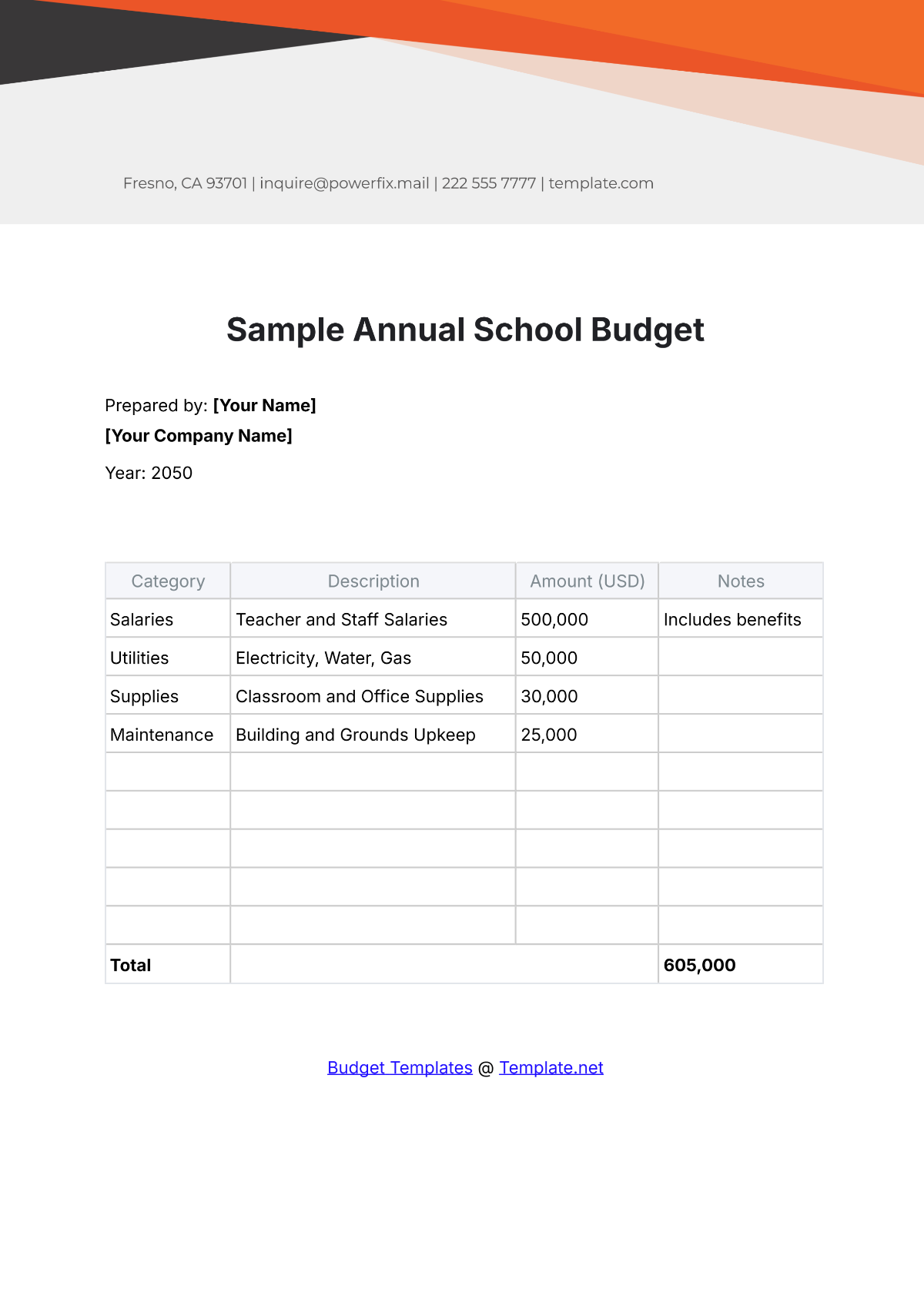
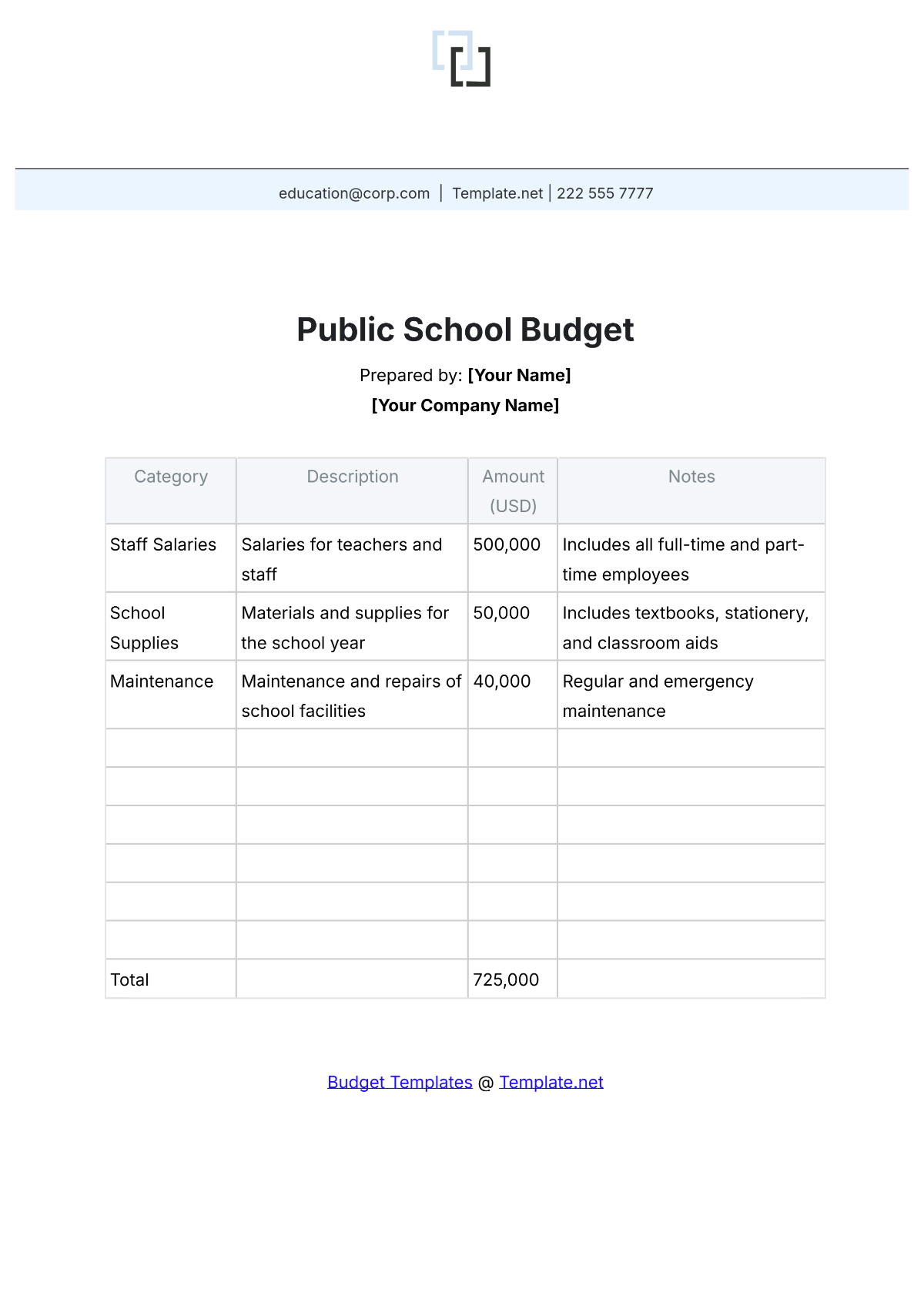
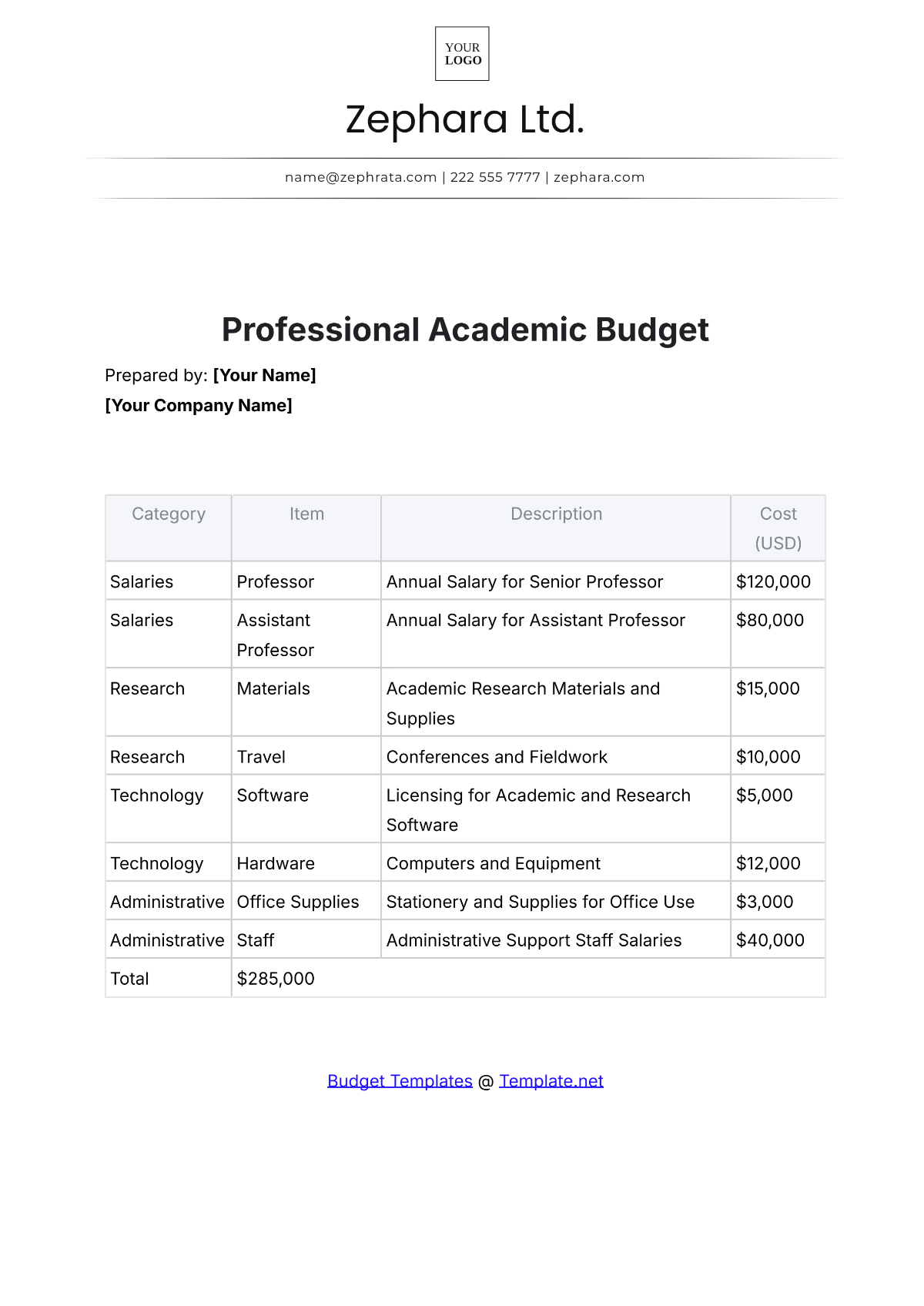
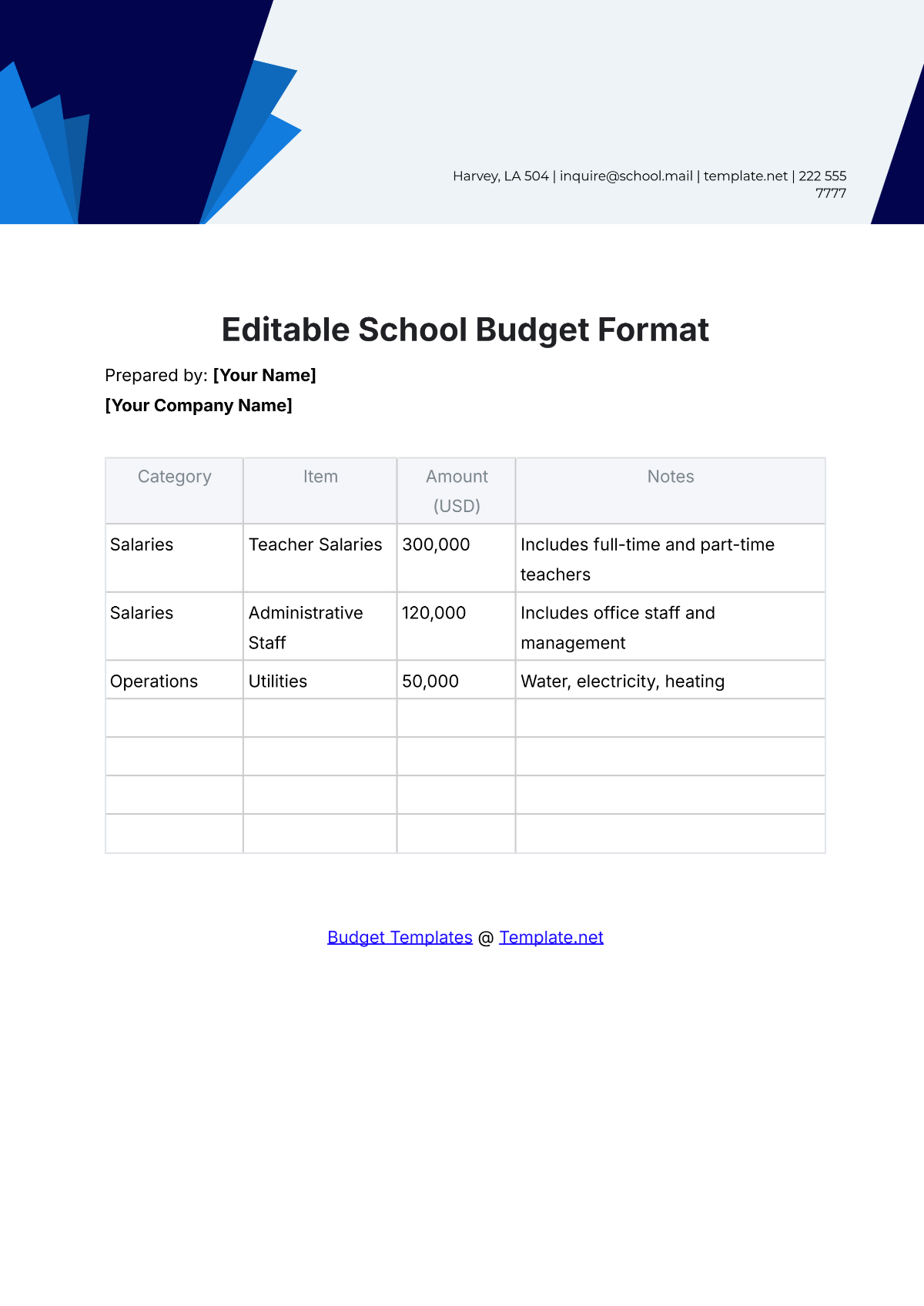
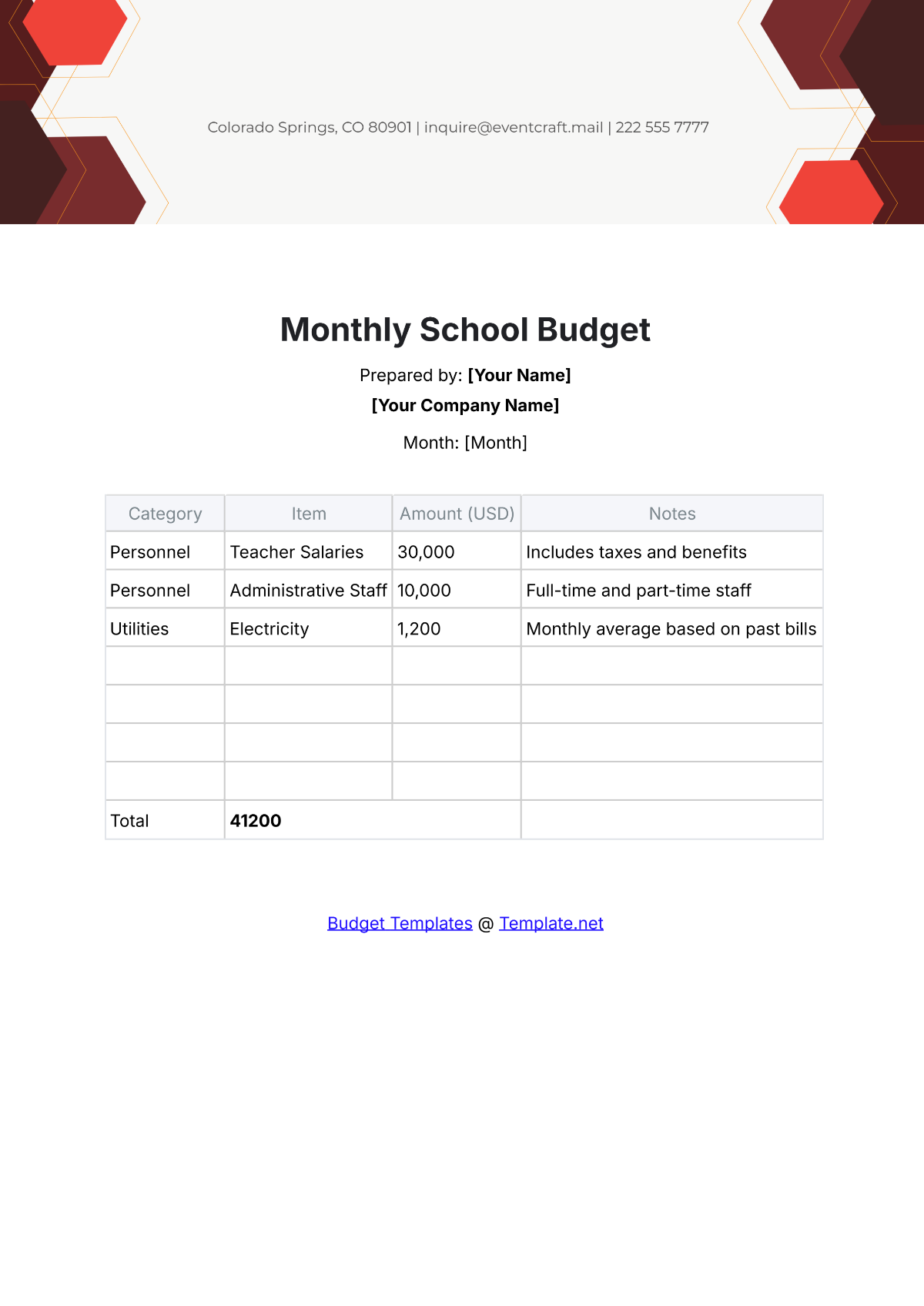
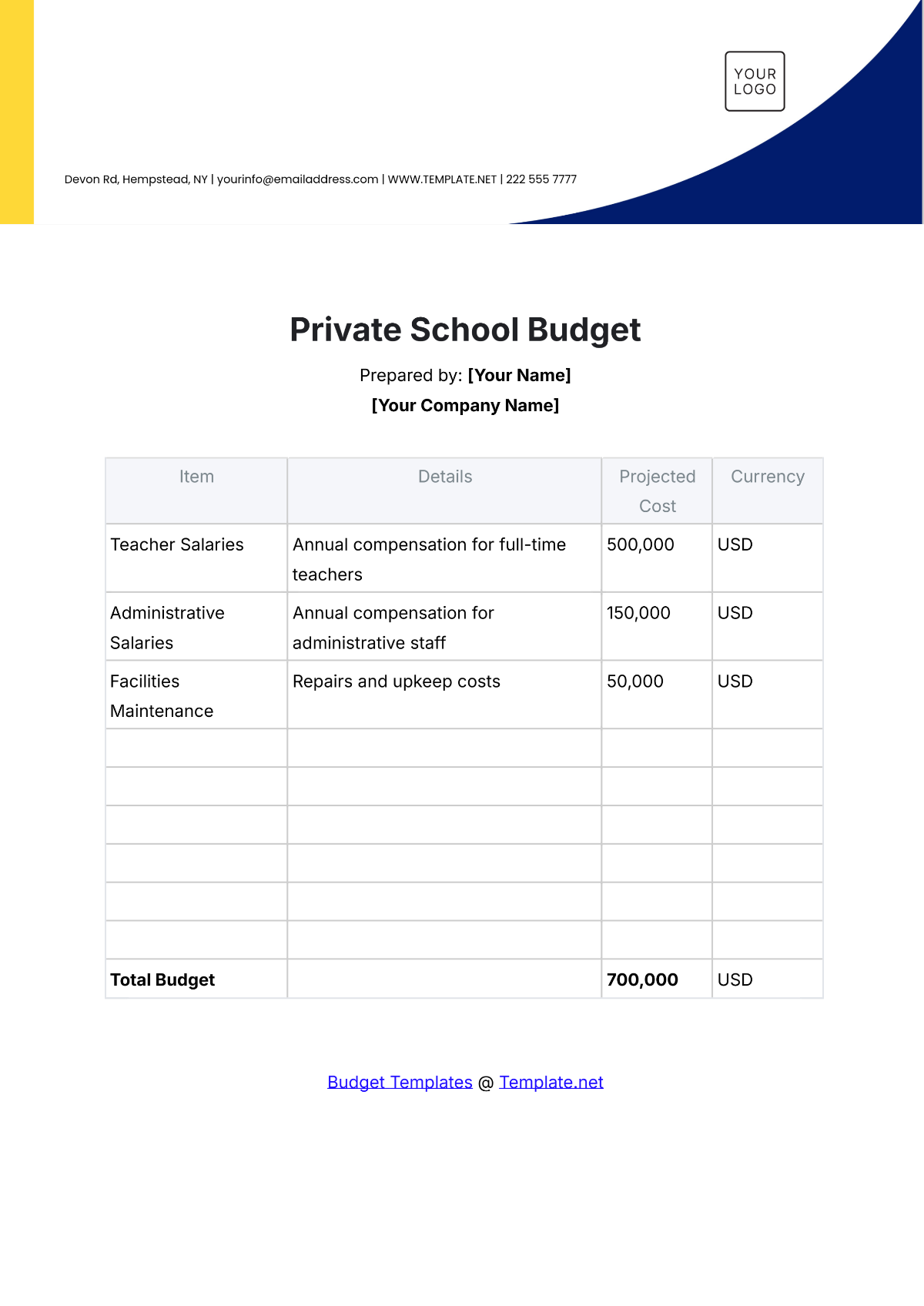
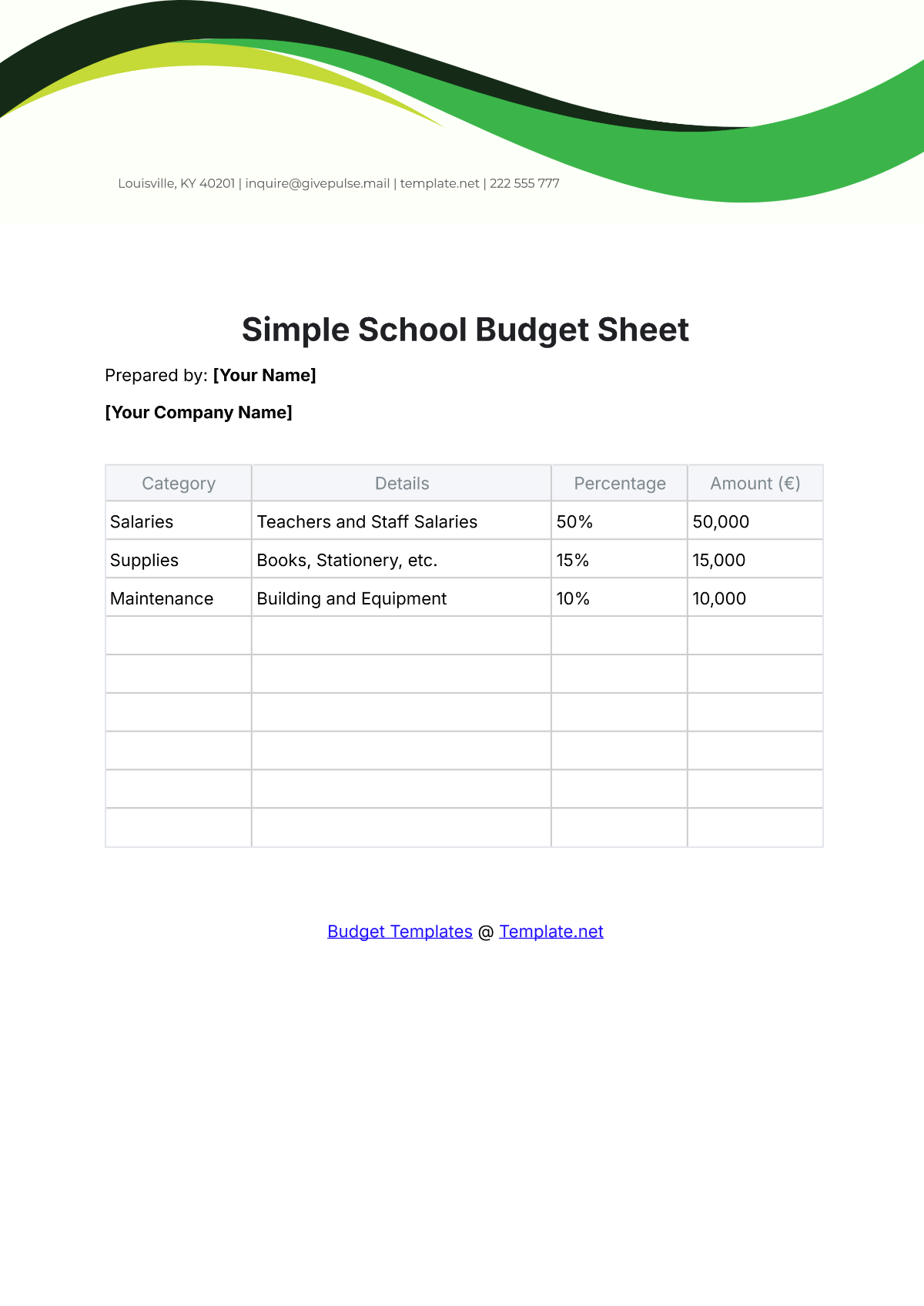
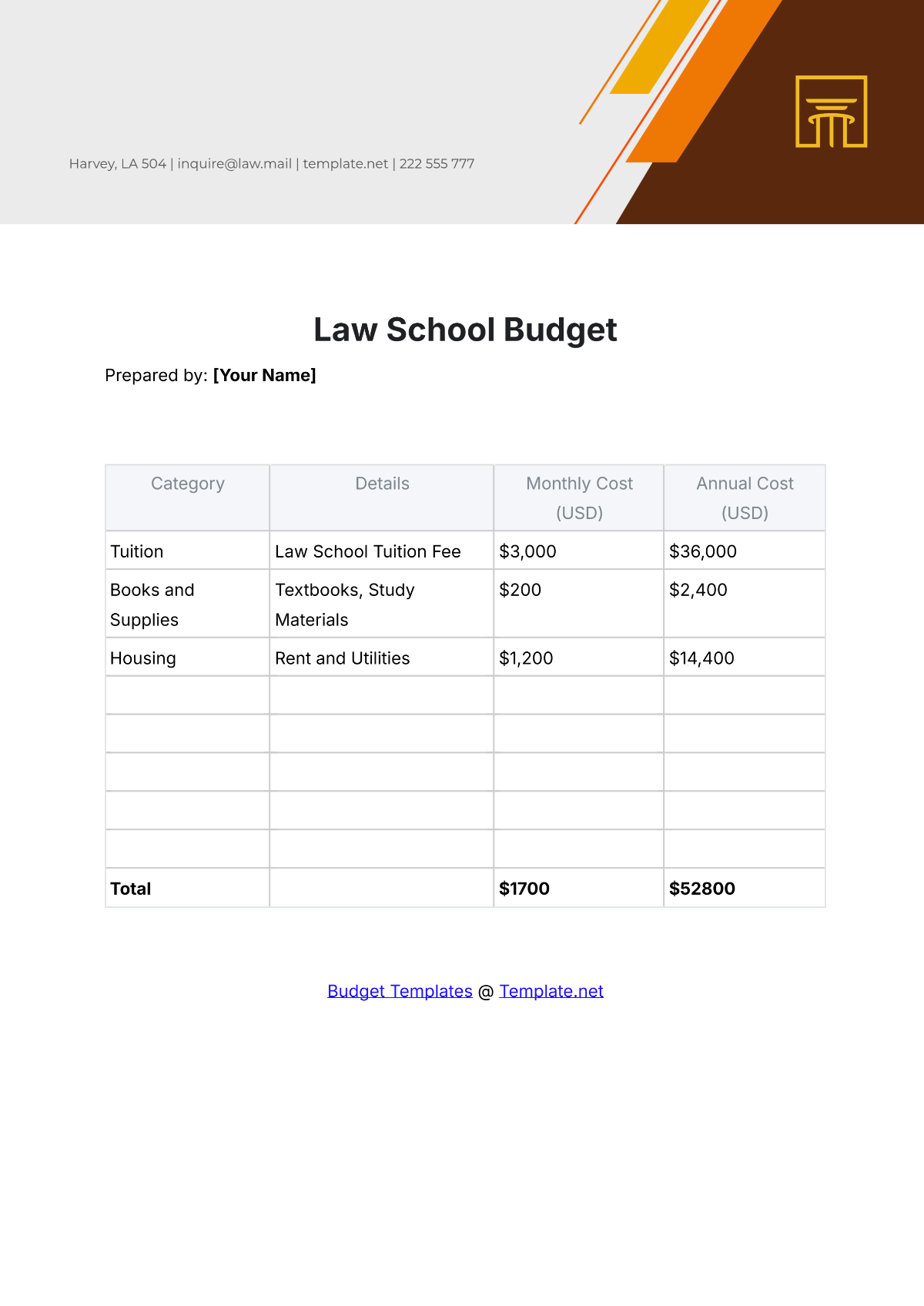
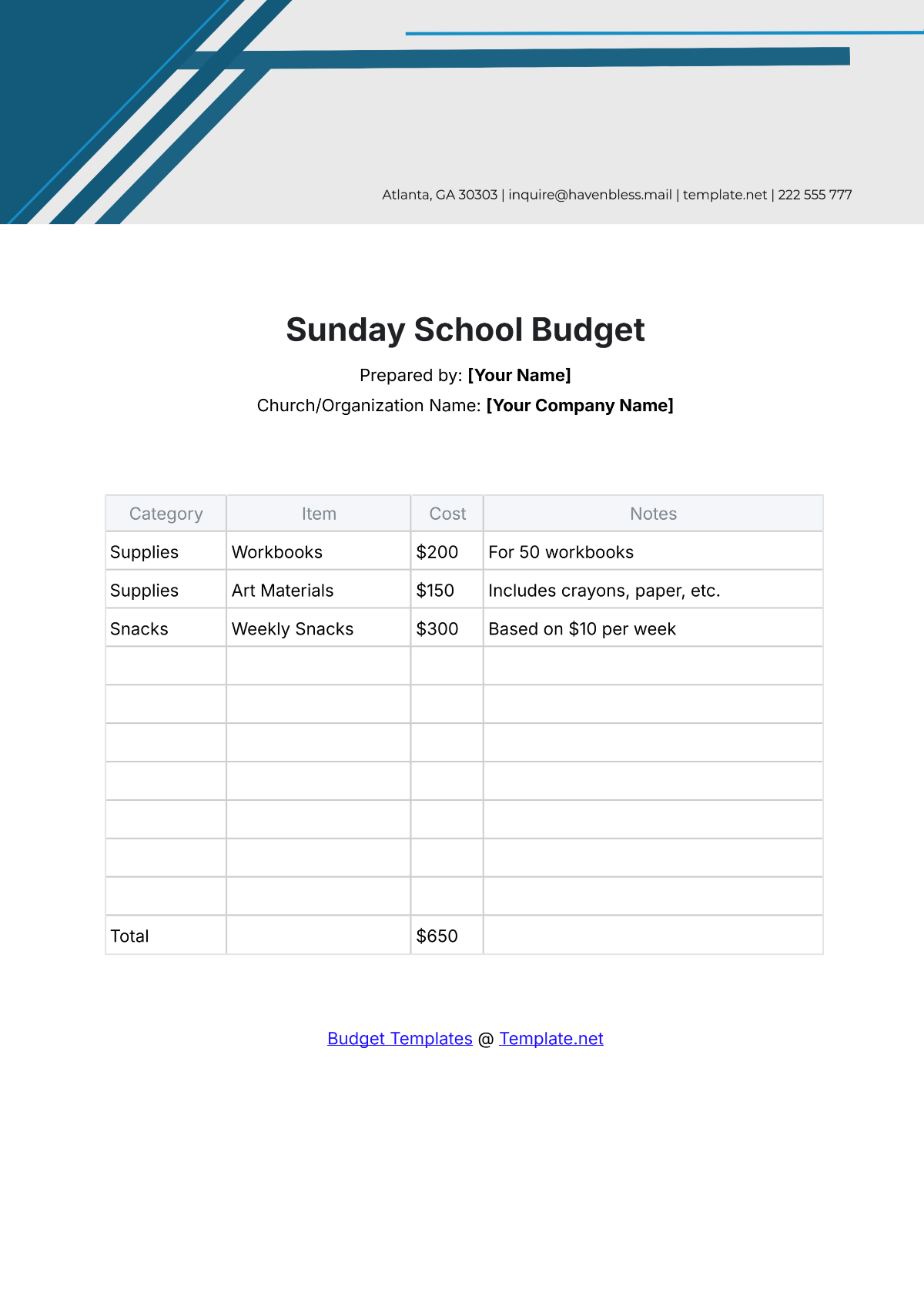
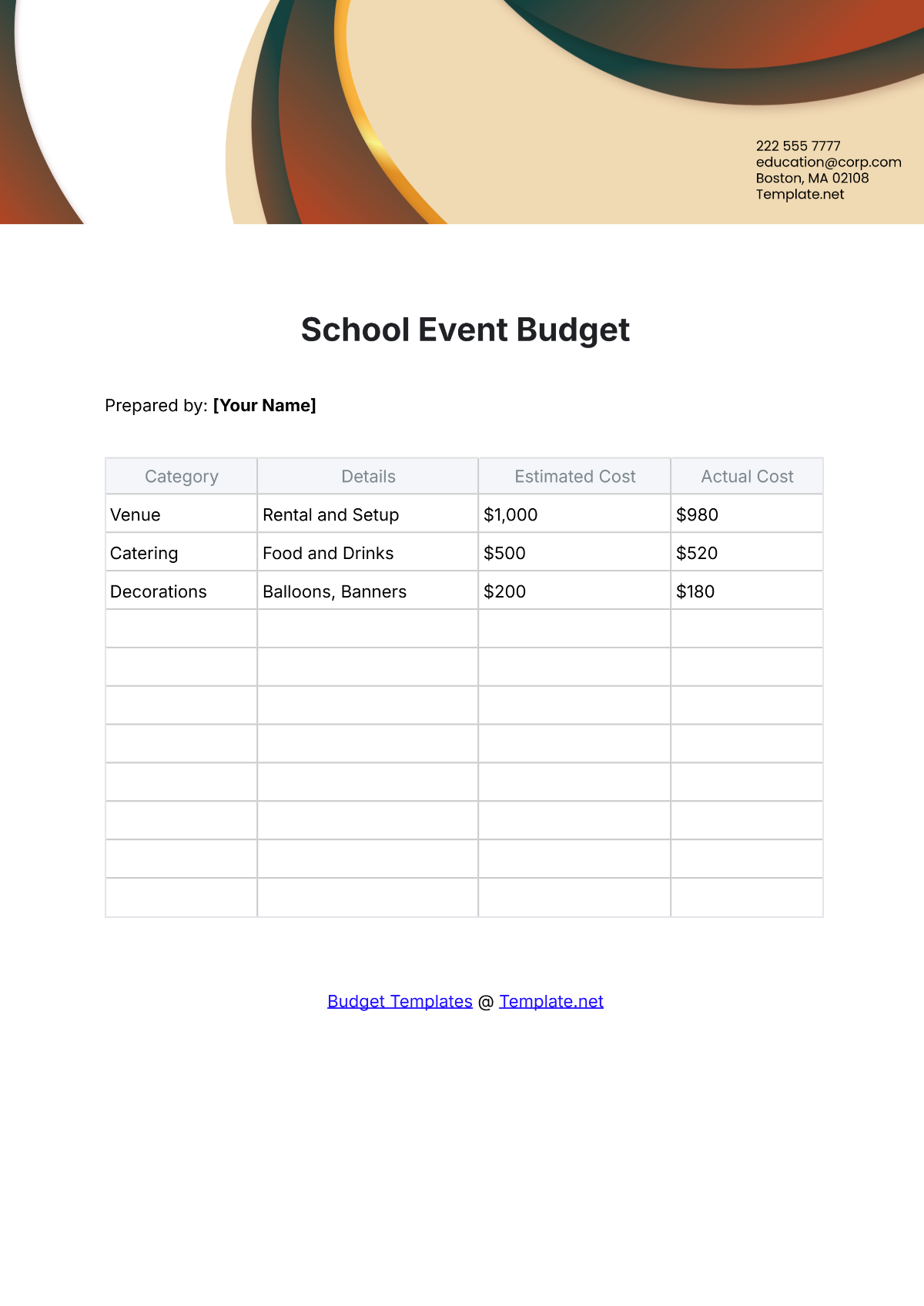
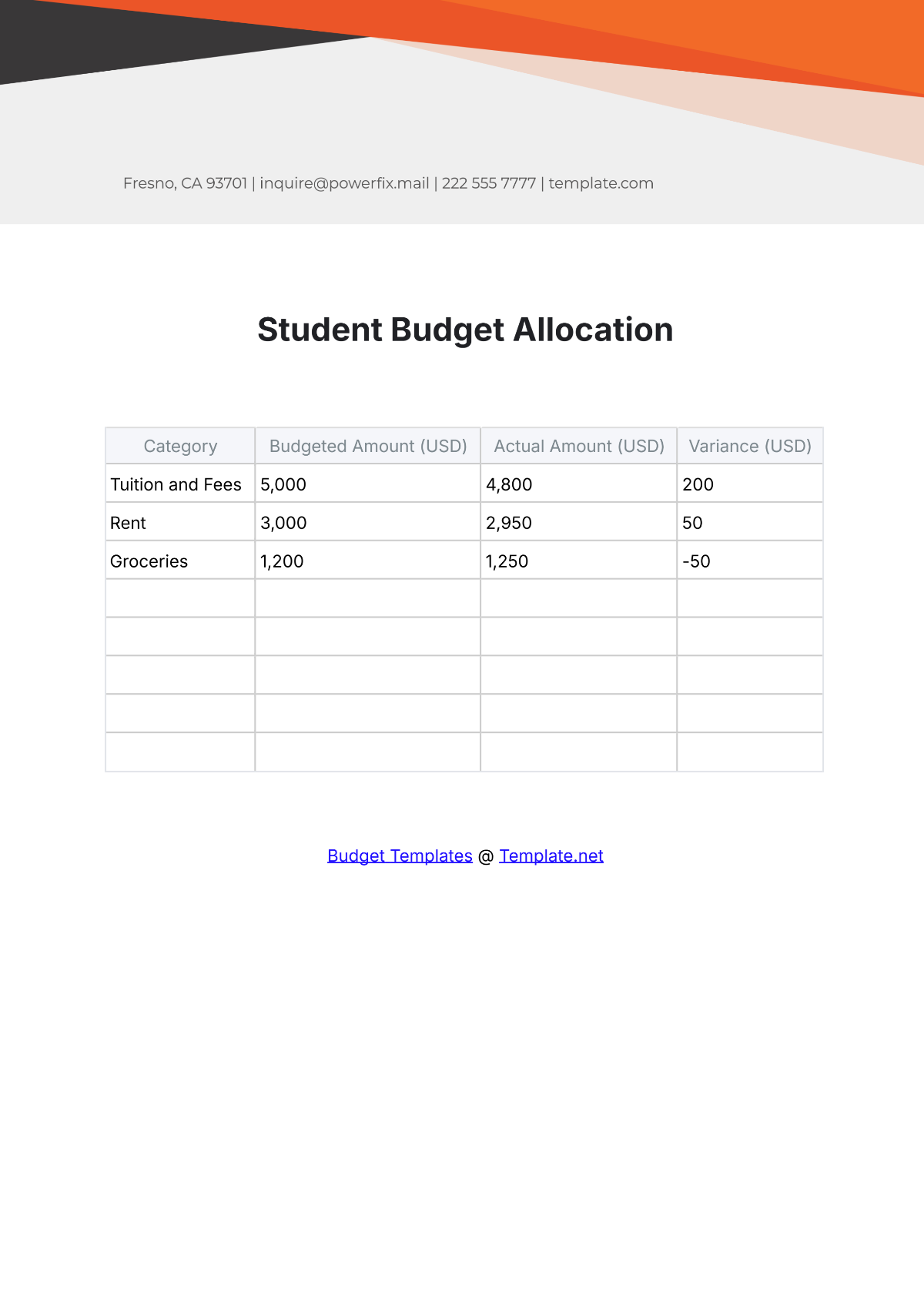
A school budget is the financial plan that outlines the anticipated revenue and expenses for a particular academic year. It serves as a roadmap for aligning financial resources with the school's mission and objectives. A strategic budget process helps in maintaining financial stability, supporting educational priorities, and setting realistic limits on resource allocation.
Steps to Creating a School Budget
1. Establish Budget Goals
Begin by setting clear budgetary goals based on both short-term and long-term educational objectives. Determine priorities such as enhancing academic programs, upgrading facilities, or investing in technology. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure effectiveness.

2. Review Past Budgets
Analyze previous years' budgets to understand spending patterns. This analysis can highlight areas of inefficiency and indicate where adjustments are needed. Compare past projections with actual expenditures to assess the accuracy of your budgeting process.
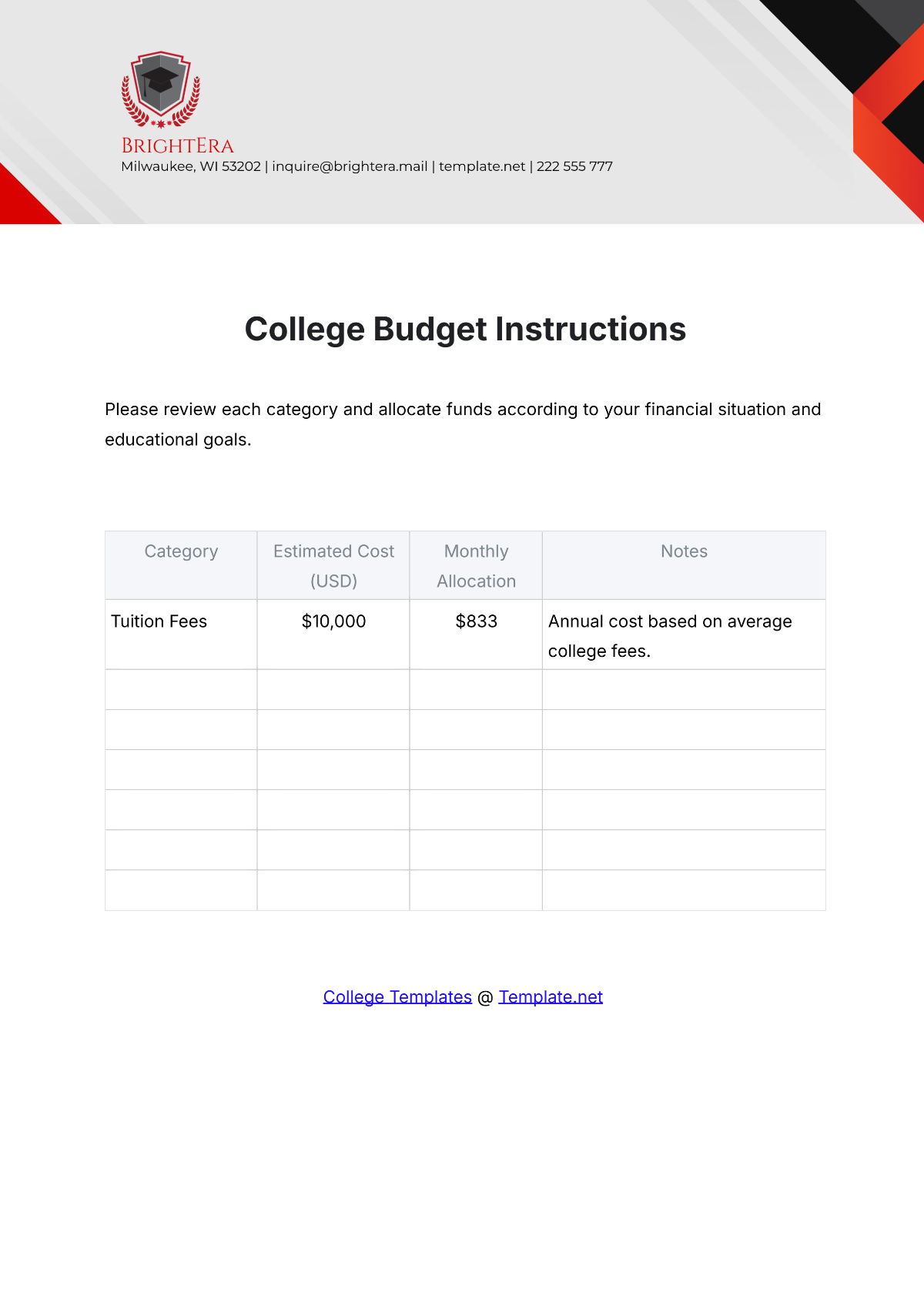
3. Forecast Revenue
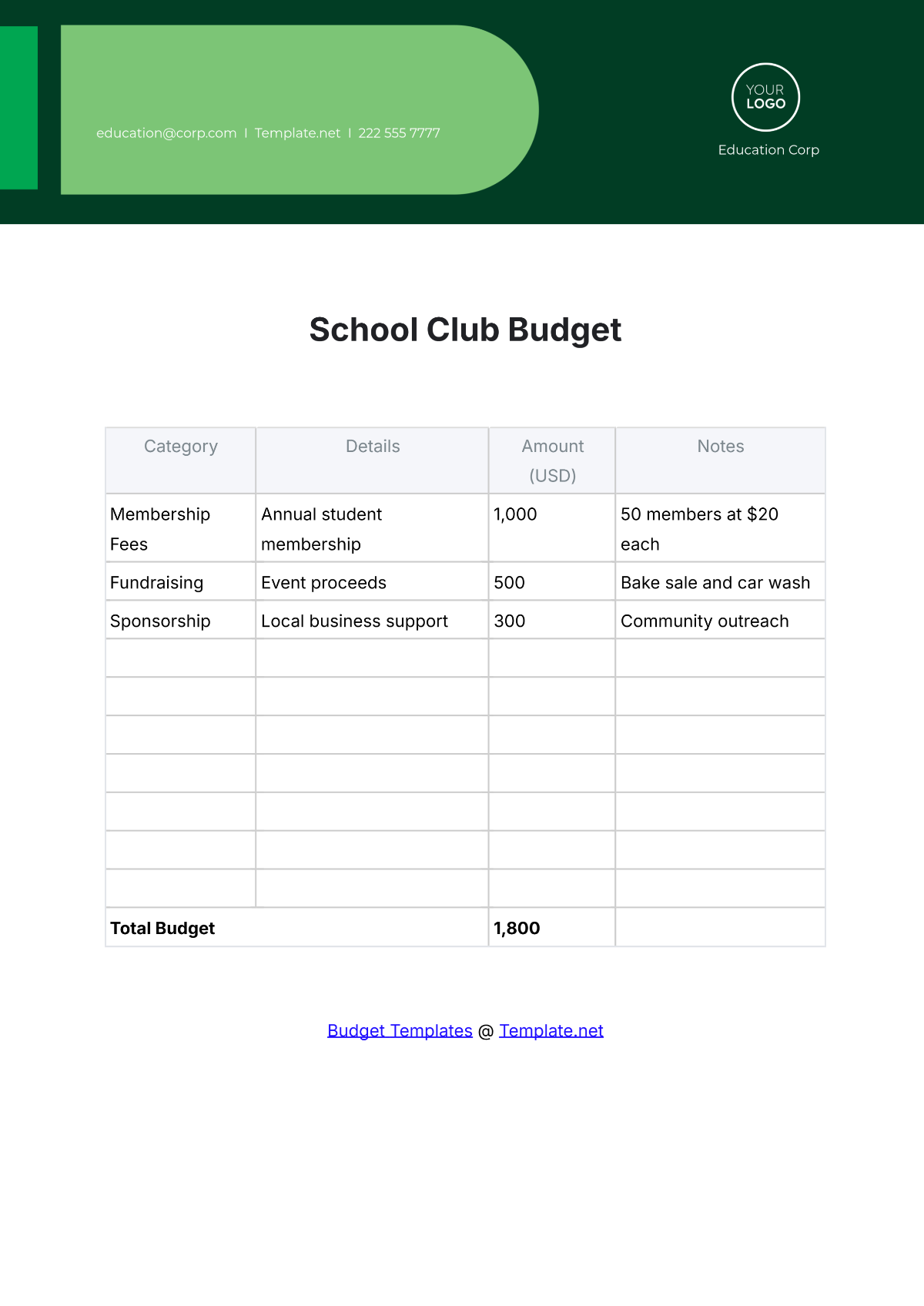
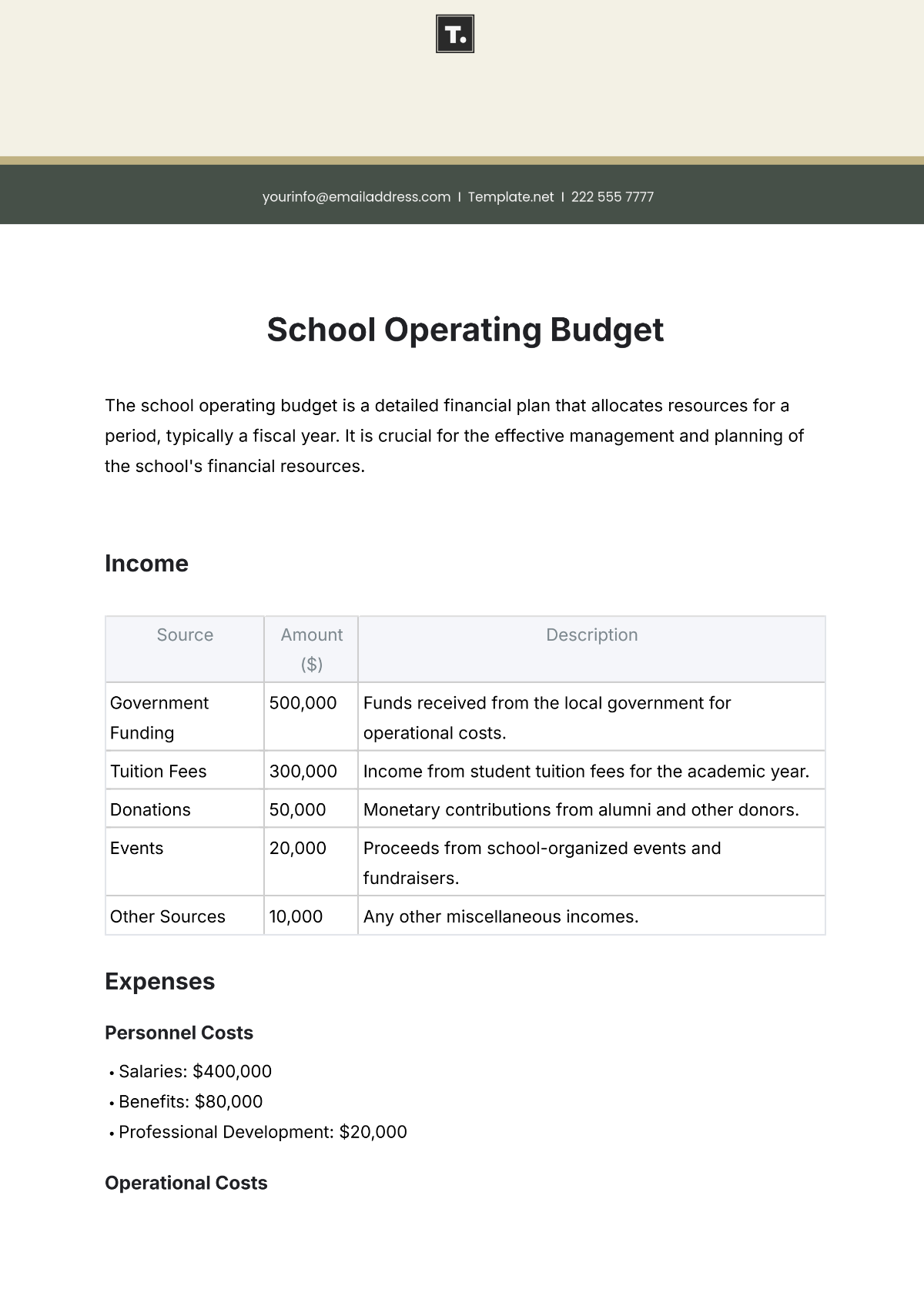
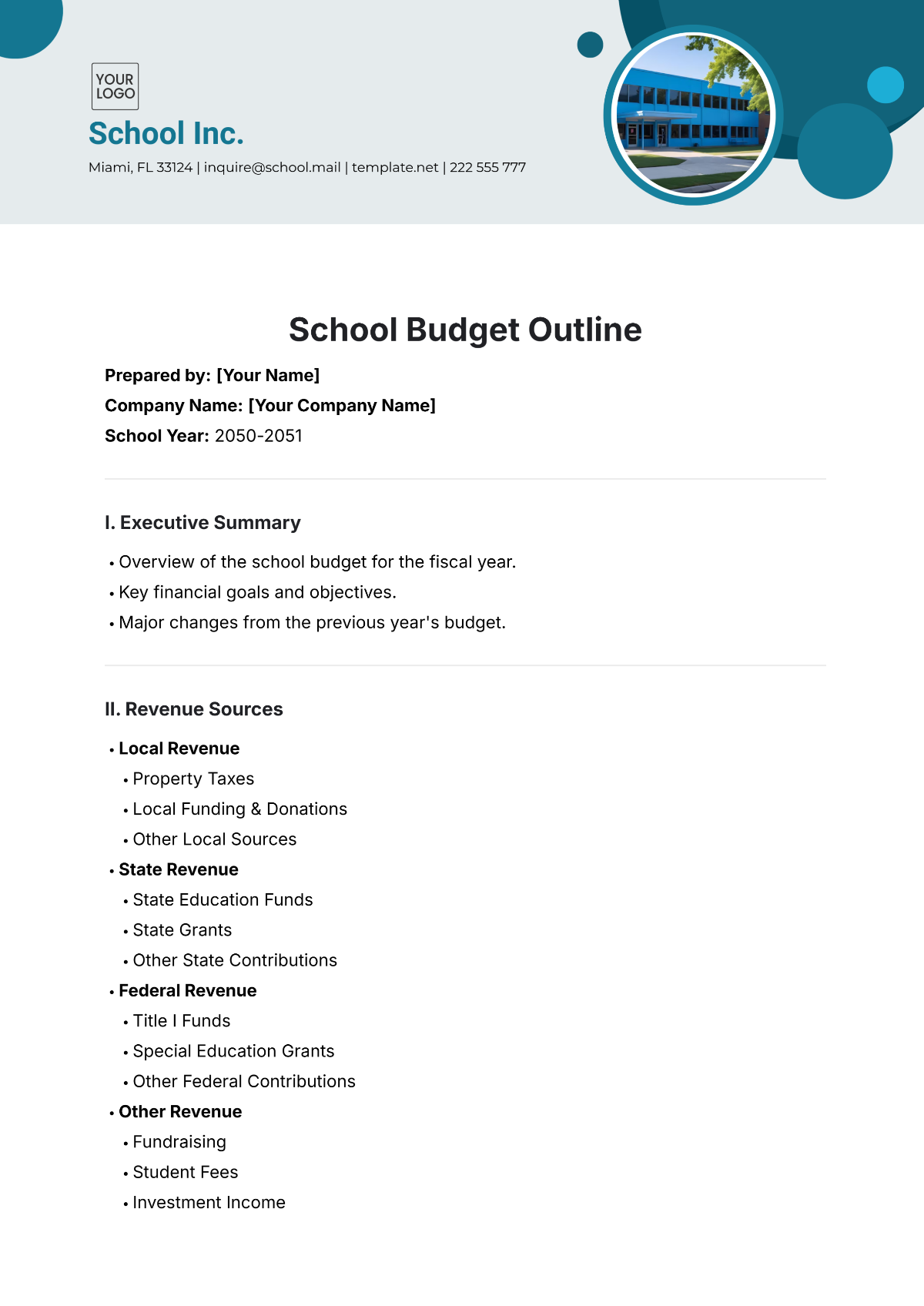
Projecting revenue is a crucial step in budget preparation. Consider all funding sources, including government allocations, grants, donations, and tuition fees. Estimating each revenue stream accurately will guide the allocation of resources effectively.
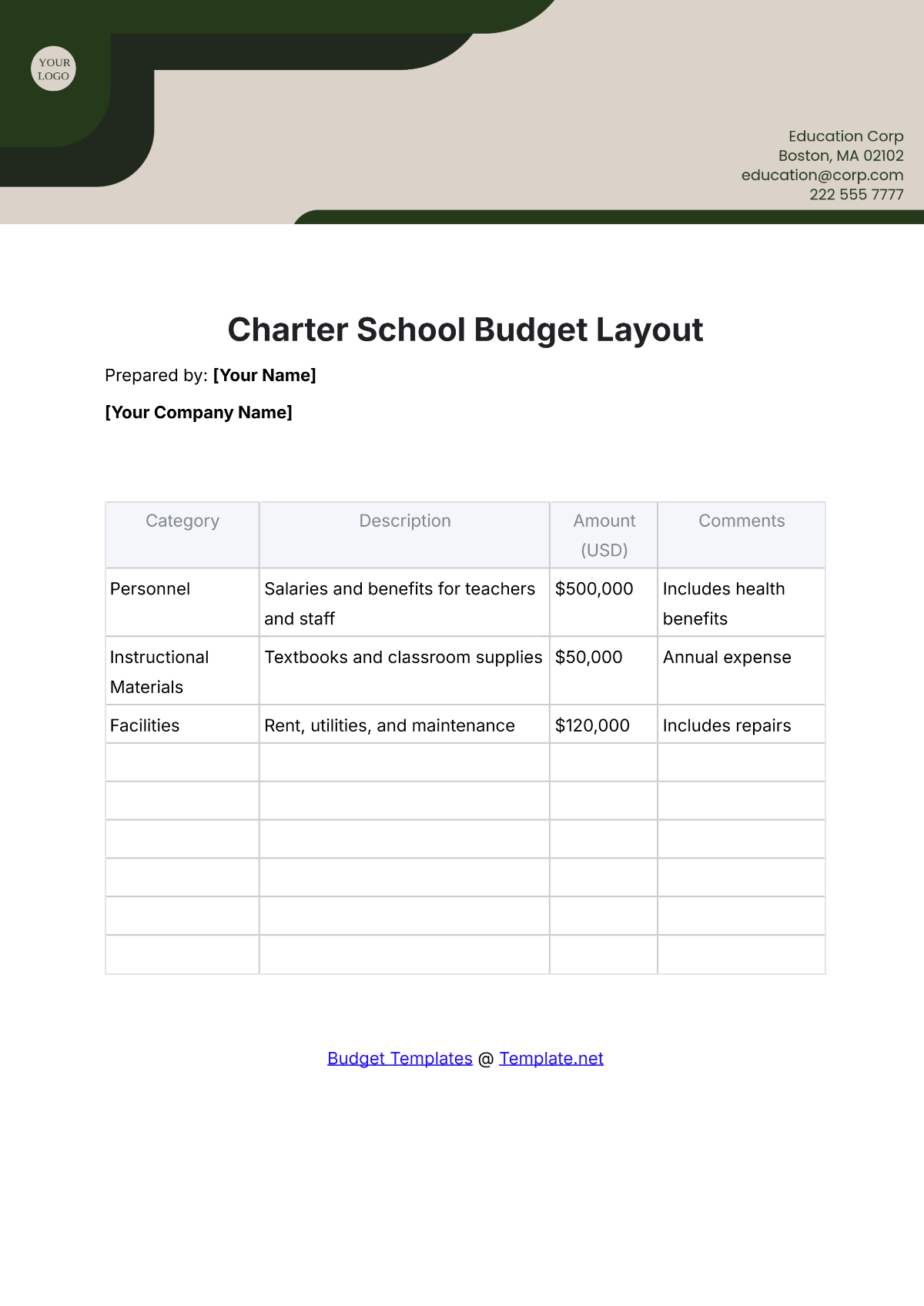
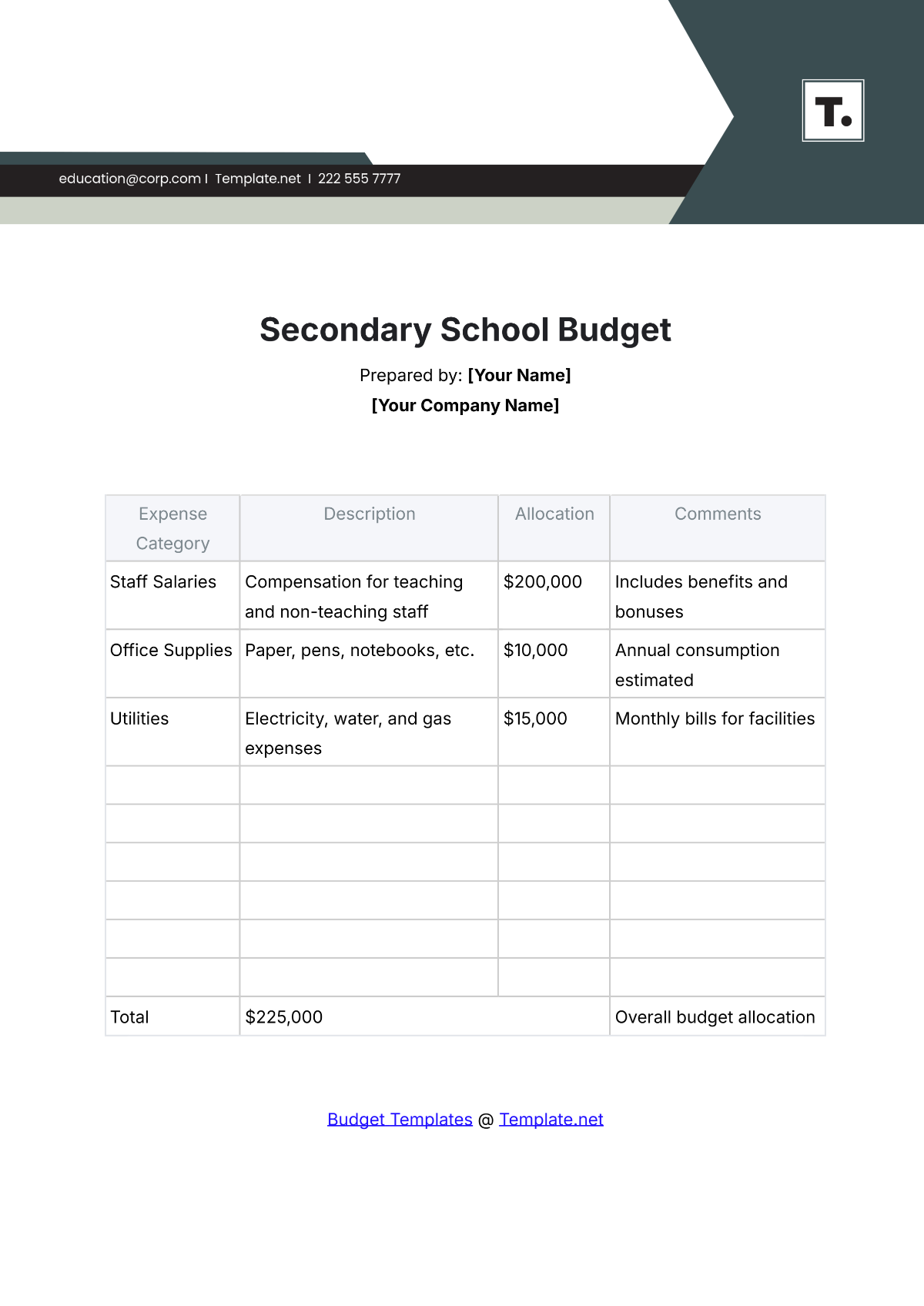
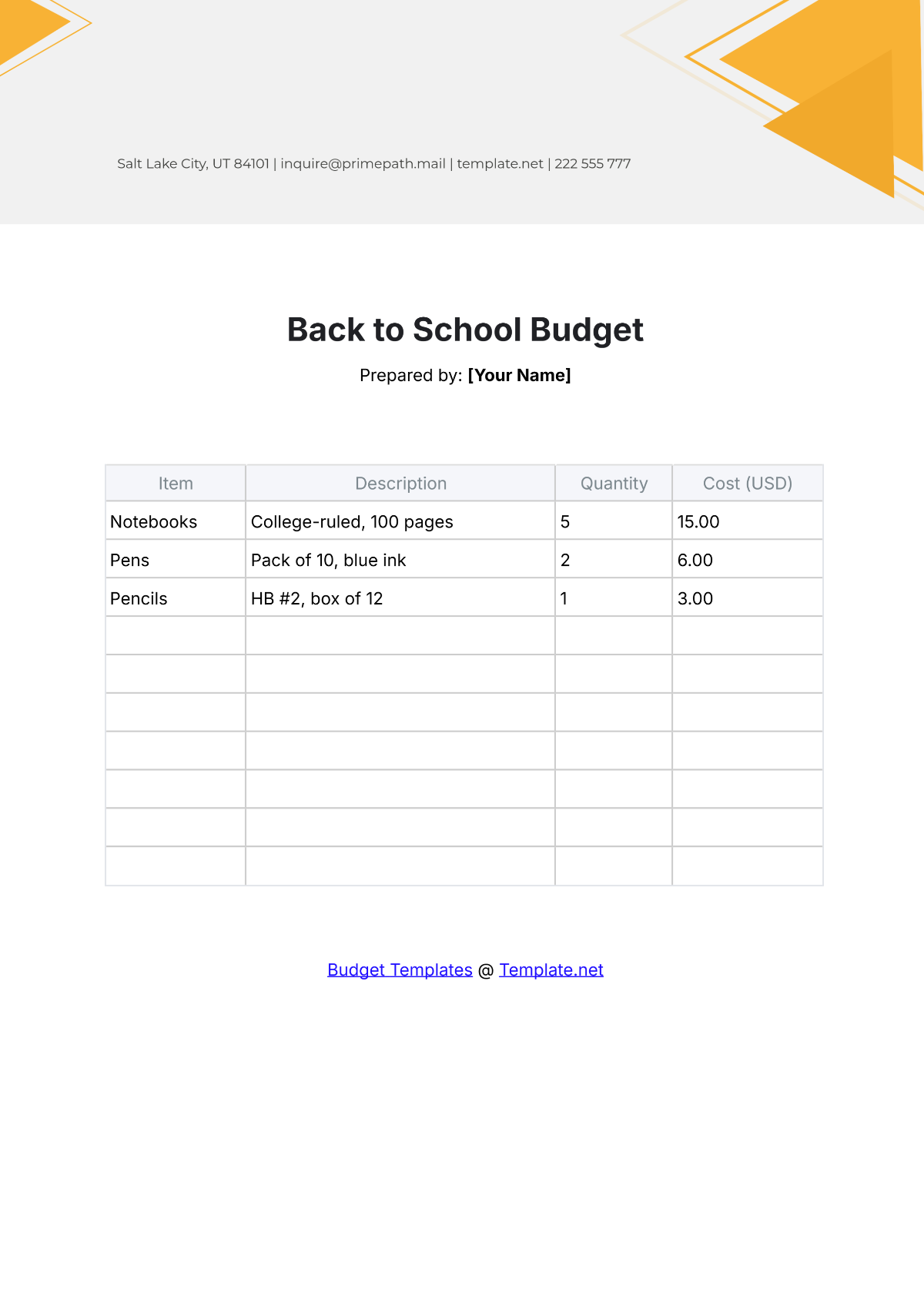
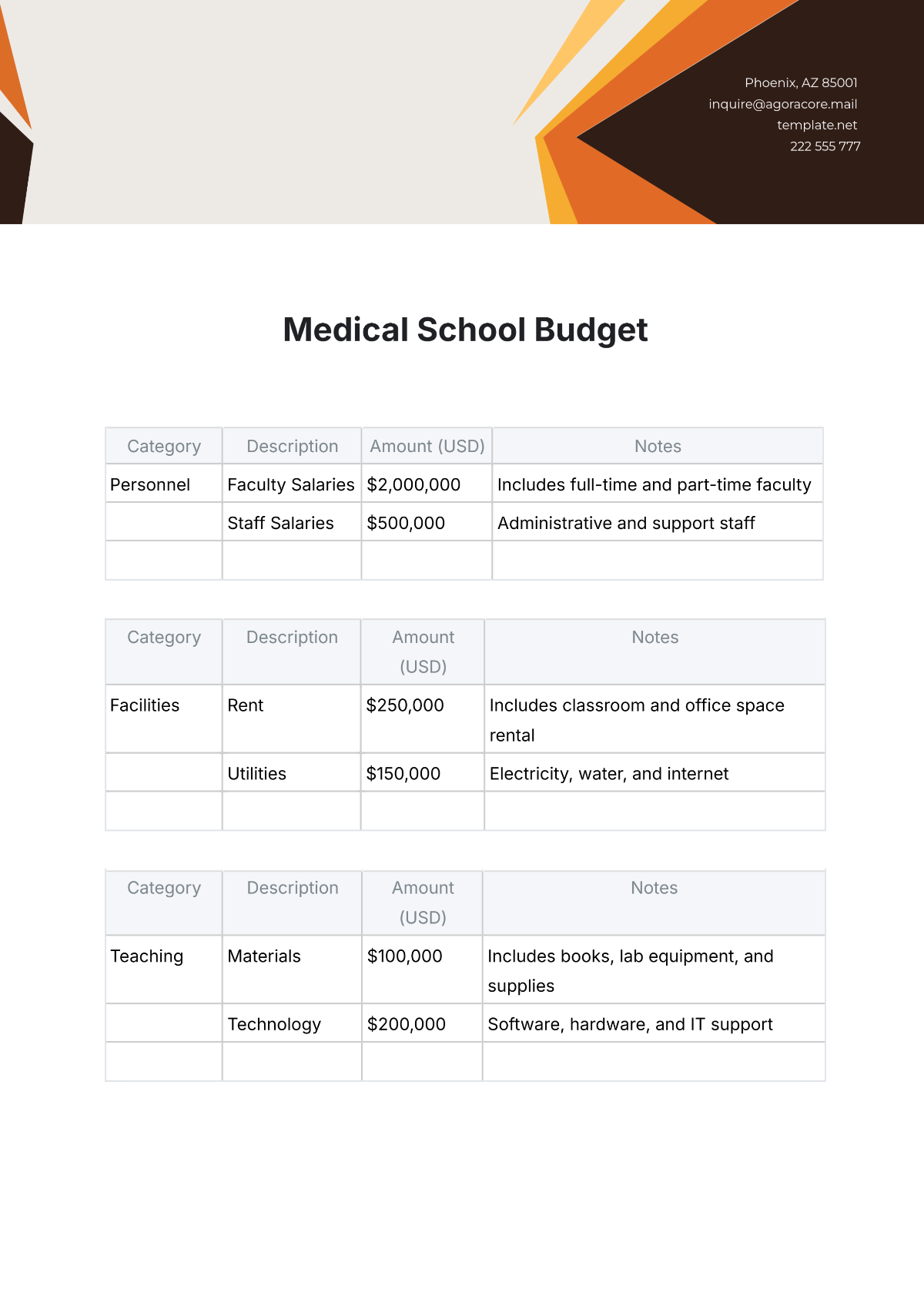
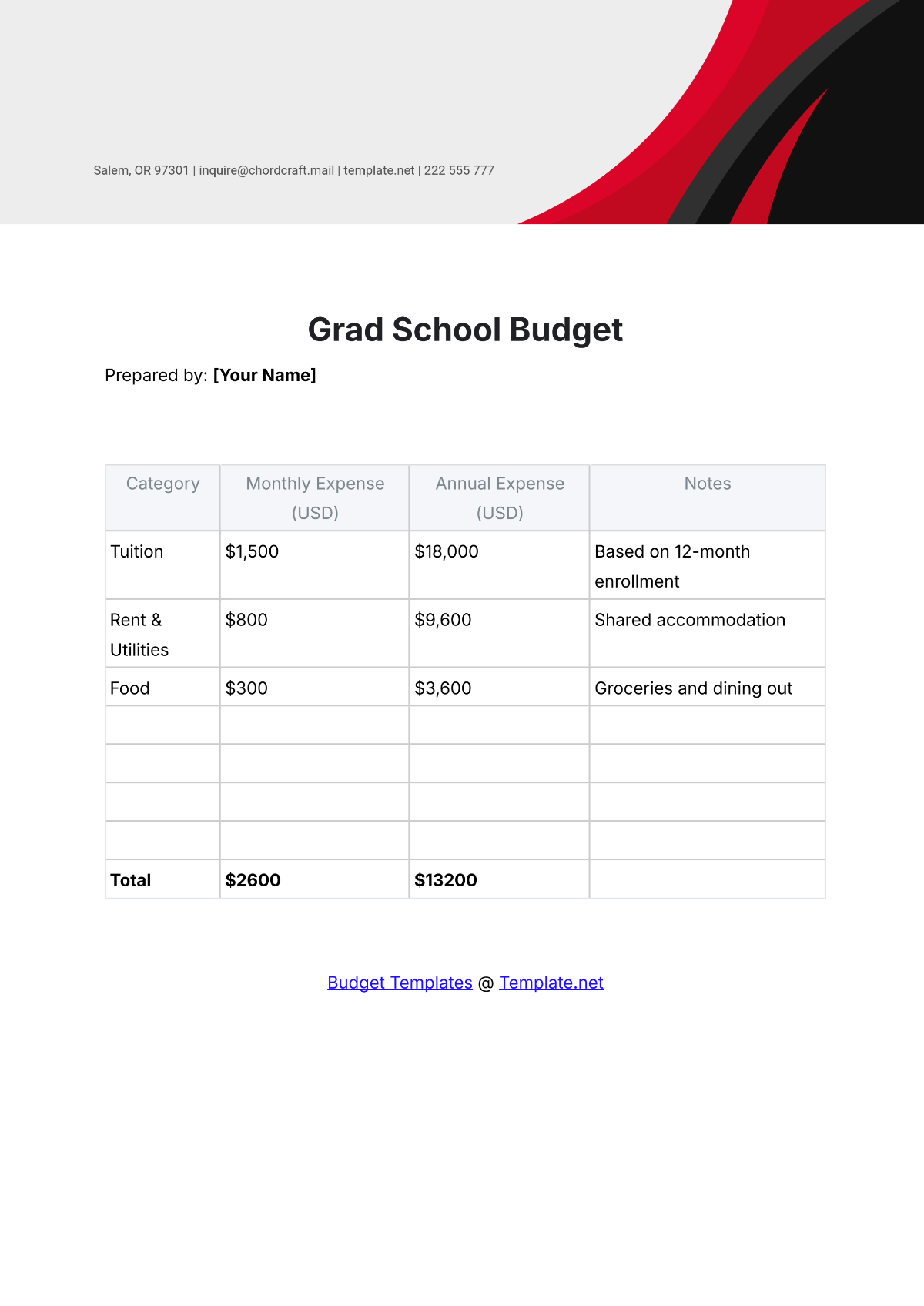
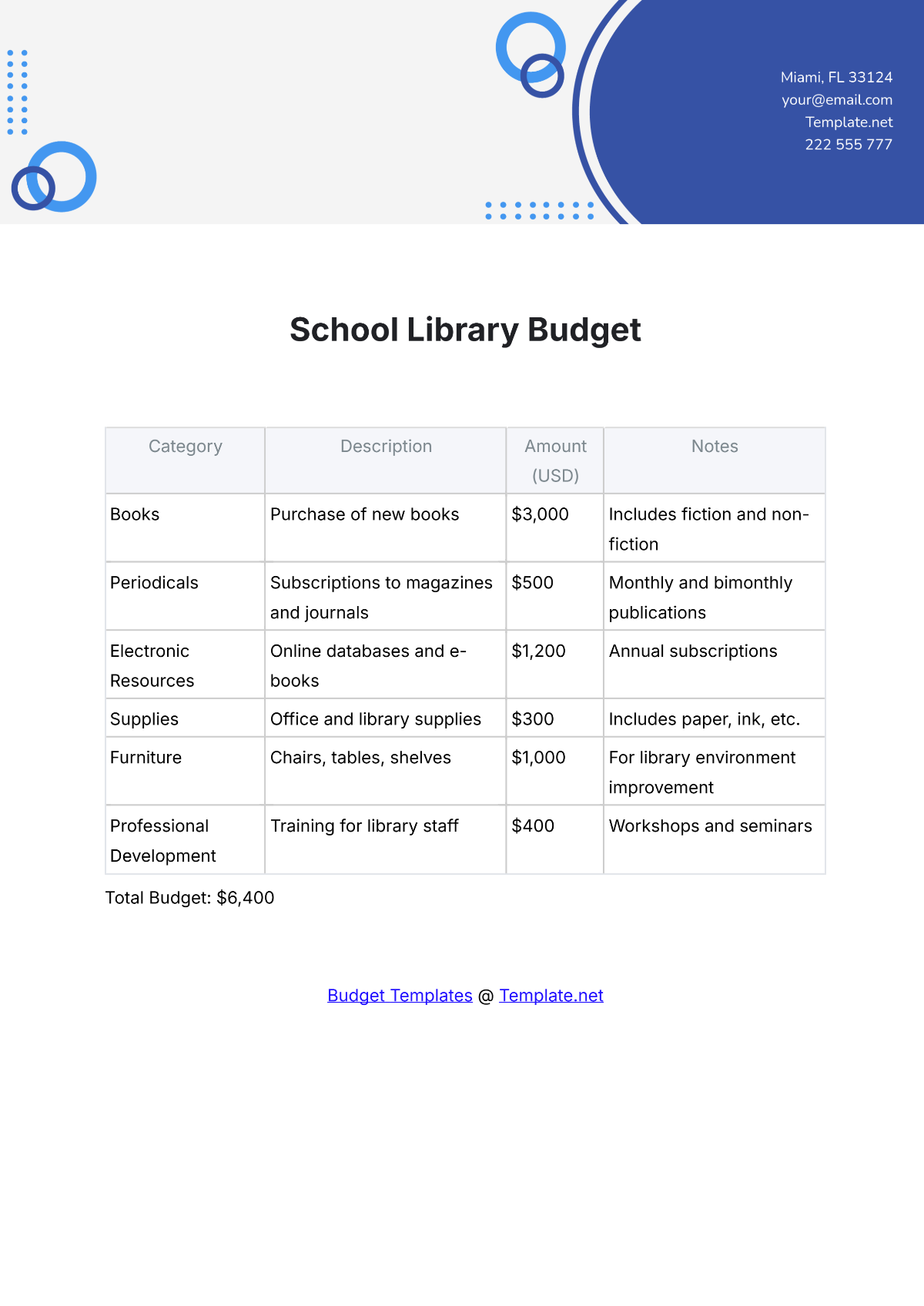
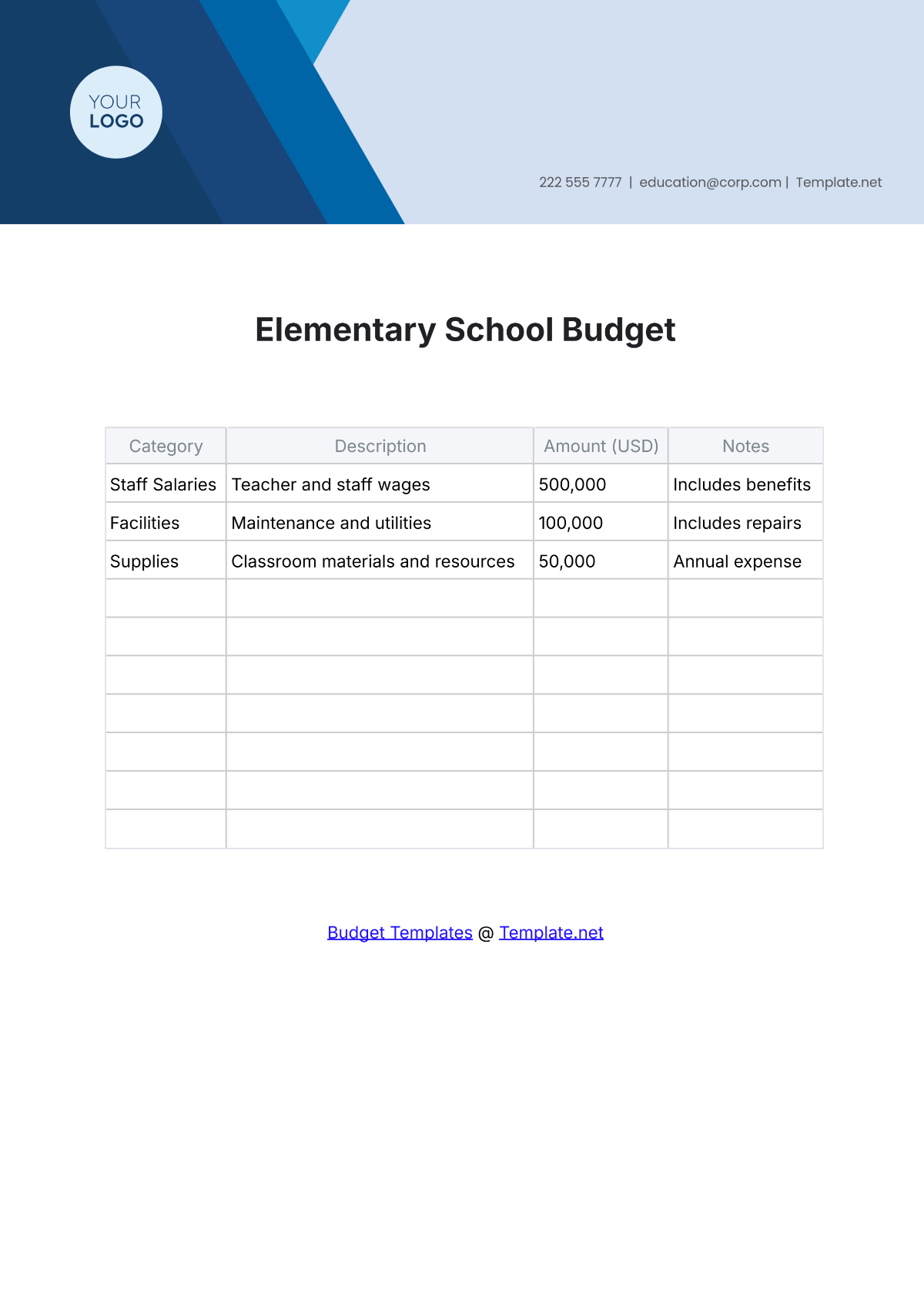
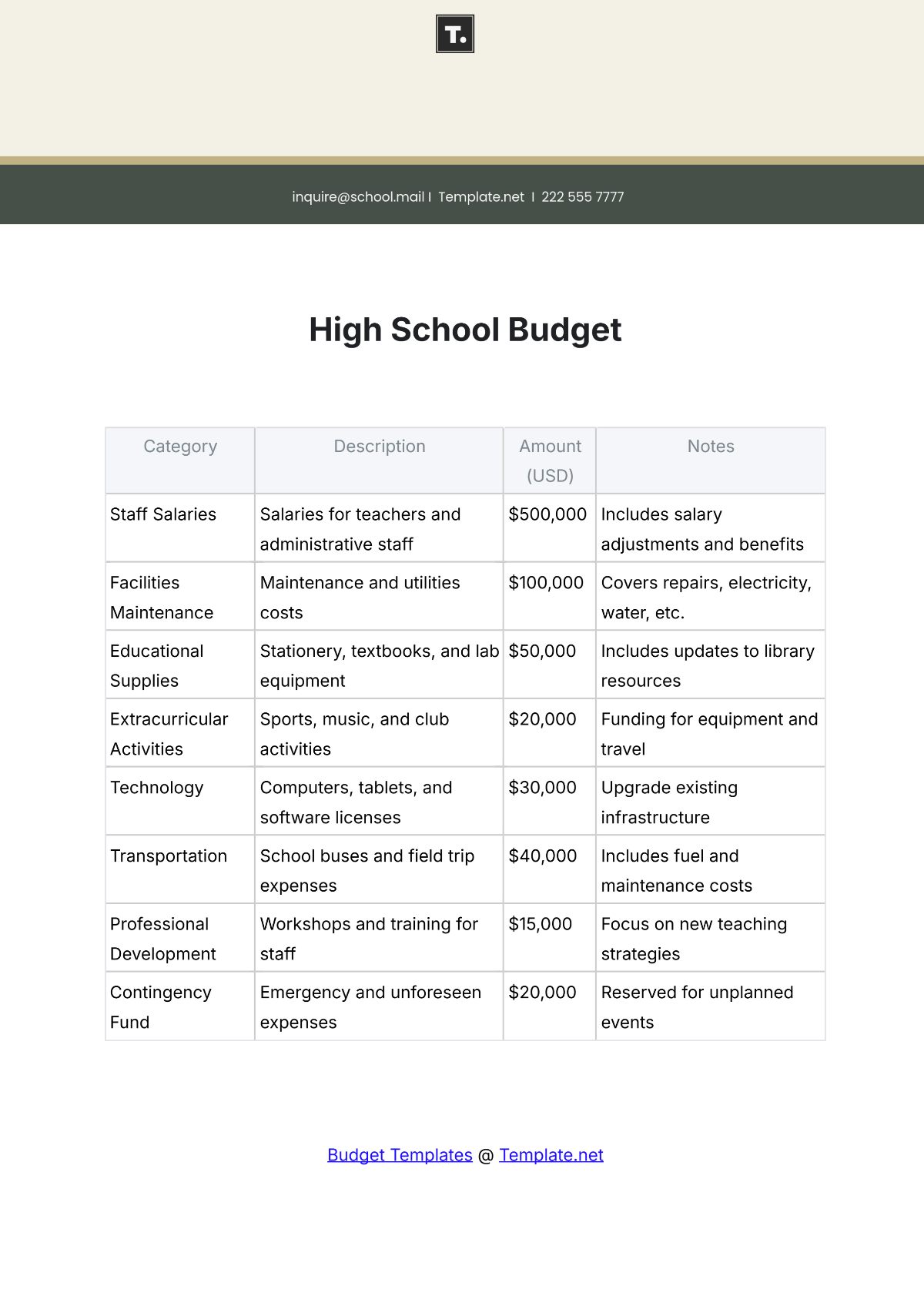
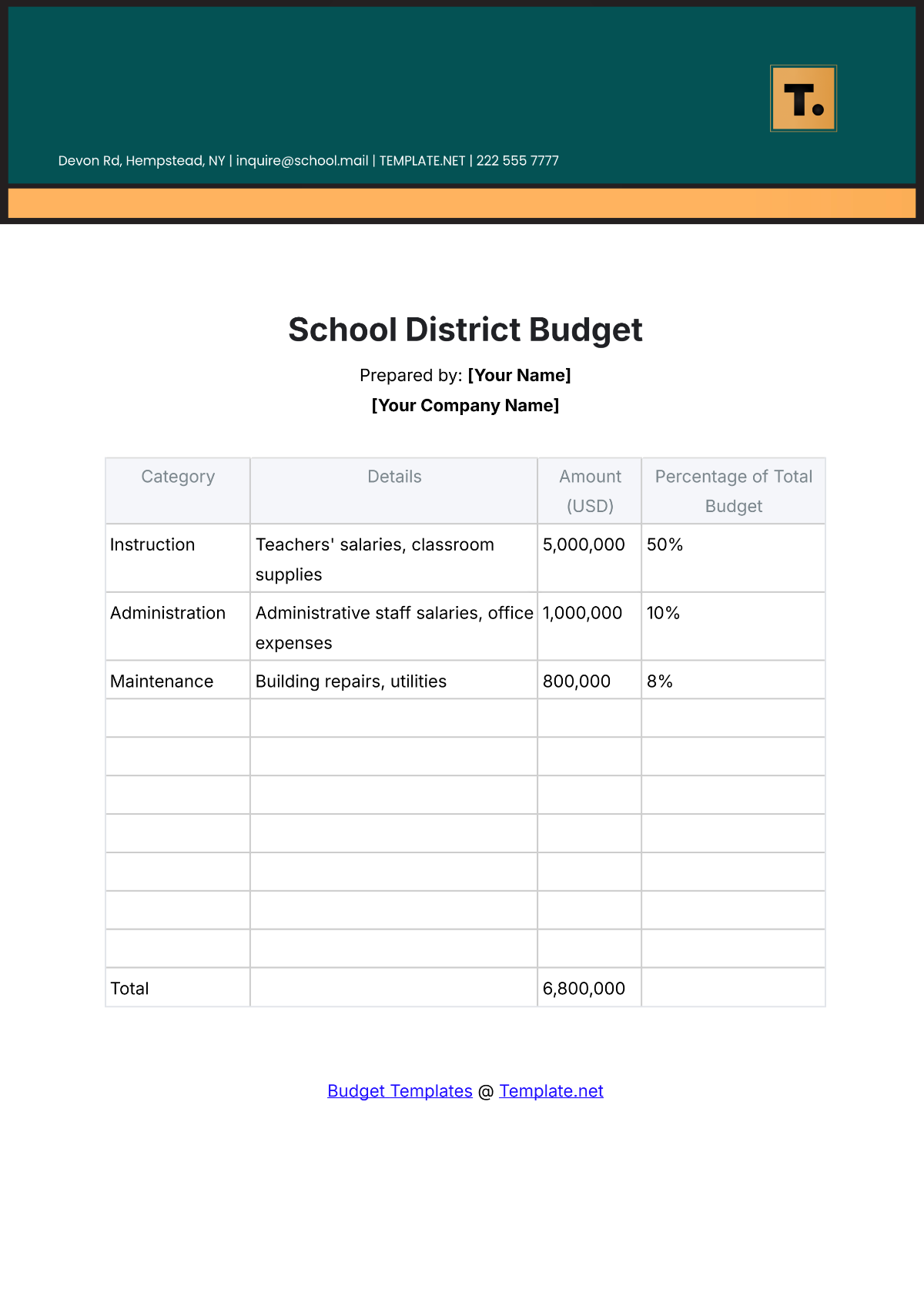
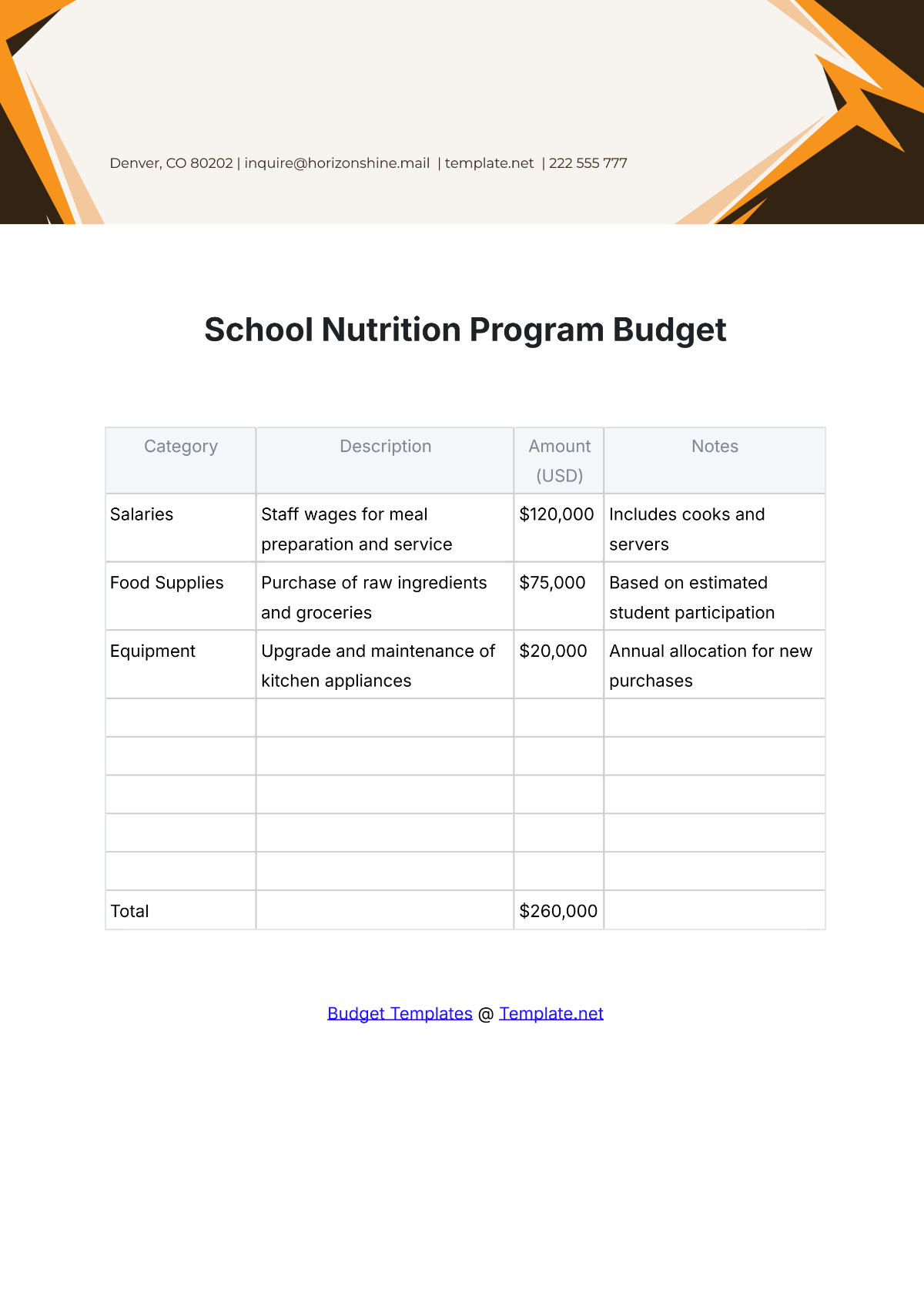
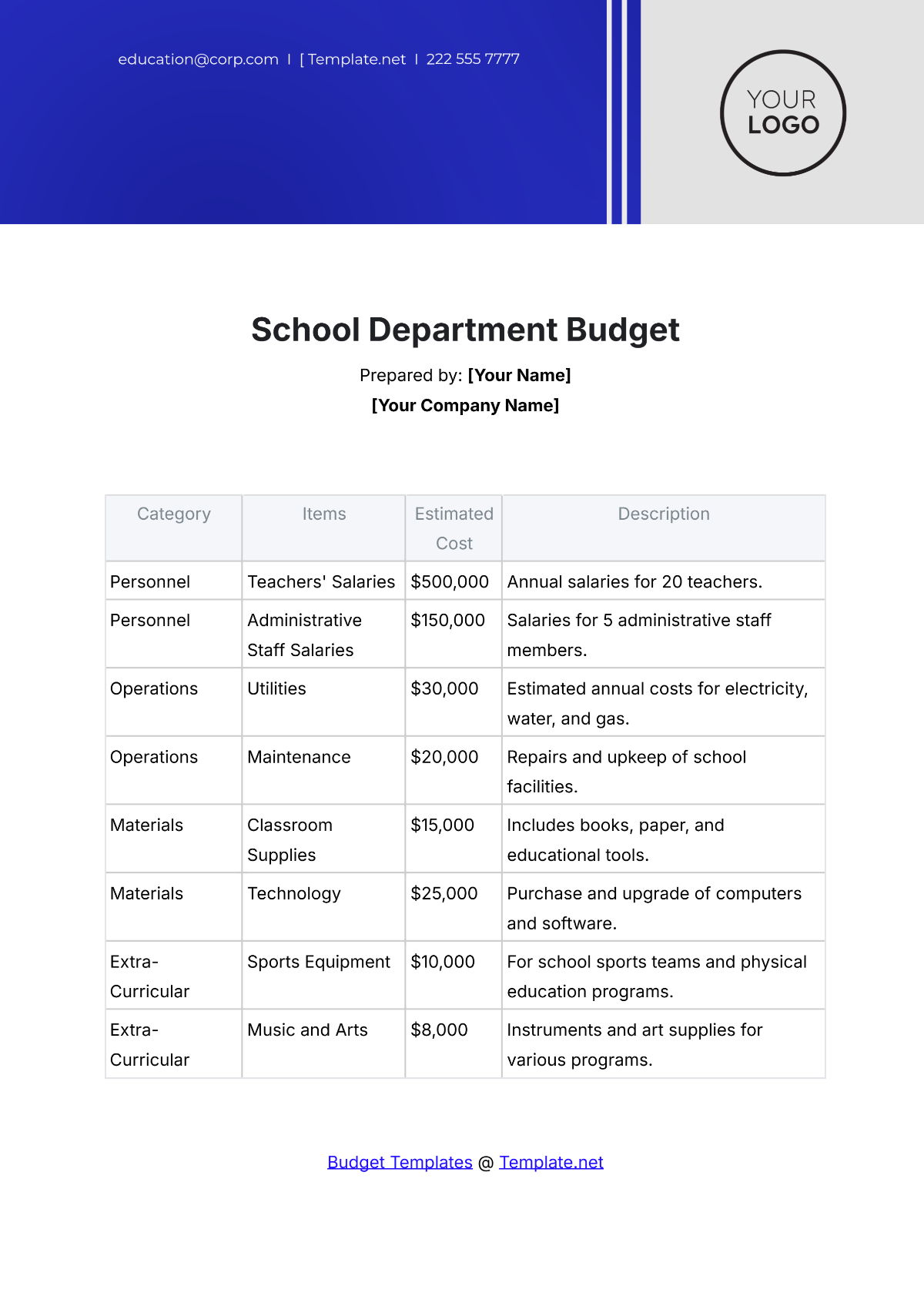
4. Identify Expenditures
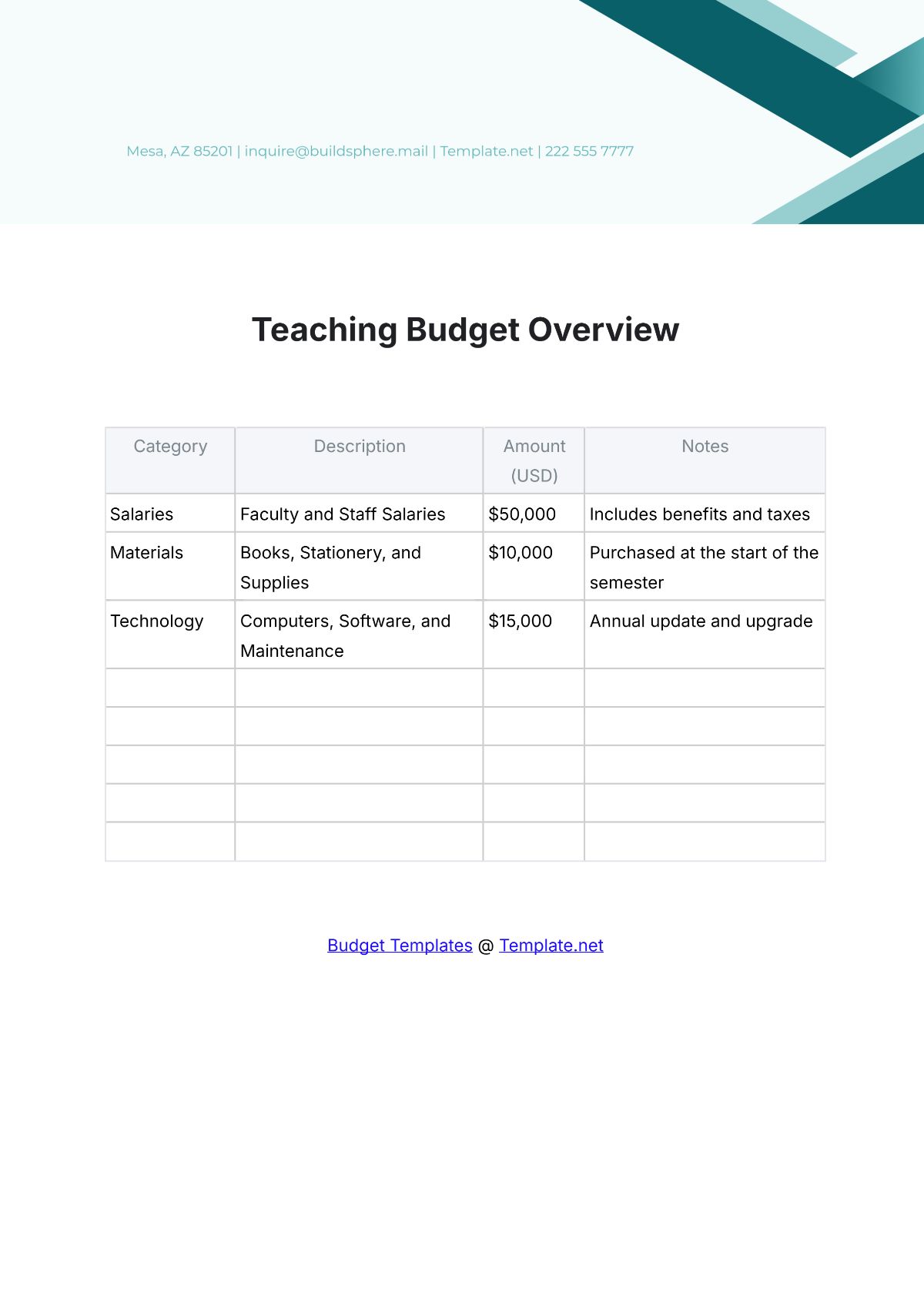
List all potential expenditures, including salaries, facilities maintenance, instructional materials, extracurricular activities, and technology upgrades. Categorize expenses as fixed (consistent) and variable (subject to change), prioritizing essential costs over discretionary spending.
5. Engage Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders such as teachers, parents, and school board members in the budgeting process. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives on resource needs and priorities, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and support for the budget plan.
6. Draft the Budget
Compile all gathered data into a draft budget document. Ensure that the budget reflects the established goals and provides a balanced representation of projected revenue and anticipated expenses. Allow for flexibility to accommodate unforeseen circumstances.

7. Review and Approve
Present the draft budget to stakeholders for feedback and approval. Engage in discussions to address any concerns and make necessary adjustments. The final budget should be a consensus document that aligns with the school's objectives and available resources.
8. Implement and Monitor
Once approved, implement the budget and monitor its execution closely throughout the academic year. Regularly reviewing expenditures against the budget helps in identifying variances early and making any necessary adjustments to avoid financial shortfalls.
Conclusion
Creating an effective school budget is an essential part of successful school management. By following these structured steps, educational institutions can ensure the efficient use of resources, support academic programs, and address the diverse needs of their students. A transparent, inclusive, and well-planned budgeting process ultimately contributes to the goal of providing quality education and fostering a productive learning environment.